{
"cells": [
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "9teObmxrP0FE"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"##### Copyright 2021 The TensorFlow Authors."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"cellView": "form",
"id": "mz8tfSwOP4fW",
"vscode": {
"languageId": "python"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"#@title Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the \"License\");\n",
"# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.\n",
"# You may obtain a copy of the License at\n",
"#\n",
"# https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0\n",
"#\n",
"# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software\n",
"# distributed under the License is distributed on an \"AS IS\" BASIS,\n",
"# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.\n",
"# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and\n",
"# limitations under the License."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "CBwpoARnQ3H-"
},
"source": [
"# 使用 SNGP 进行不确定性感知深度学习"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "2dL6_obQRBGQ"
},
"source": [
""
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "UvW1QEMtP7Gy"
},
"source": [
"在诸如医疗决策制定和自动驾驶等安全性至关重要的 AI 应用中,或者在数据存在固有噪声的情况(例如自然语言理解)下,深度分类器必须能够可靠地量化其不确定性。深度分类器应能感知到自身的局限性,并能意识到何时应将控制权交给人类专家。本教程展示了如何使用称为**谱归一化神经高斯过程 ([SNGP](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.10108){.external})** 的技术来提高深度分类器量化不确定性的能力。\n",
"\n",
"SNGP 的核心思想是通过对网络应用简单的修改来提高深度分类器的***距离感知***。模型的*距离感知*是衡量其预测概率能否准确反映测试样本与训练数据间距离的指标。这是黄金标准下的概率模型(例如,具有 RBF 内核的[高斯过程](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gaussian_process){.external})常需的属性,但在具有深度神经网络的模型中却缺少这一属性。SNGP 提供了一种将这种高斯过程行为注入到深度分类器中,同时能够保持其预测准确率的简单方式。\n",
"\n",
"本教程在 [scikit-learn 的双月](https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.datasets.make_moons.html){.external} 数据集上实现了一个基于深度残差网络 (ResNet) 的 SNGP 模型,并将其不确定性表面与其他两种热门不确定性方式的不确定性表面进行比较:[蒙特卡罗随机失活](https://arxiv.org/abs/1506.02142){.external} 和[深度集成](https://arxiv.org/abs/1612.01474){.external}。\n",
"\n",
"本教程例举了基于小型 2D 数据集的 SNGP 模型。有关使用 BERT-base 将 SNGP 应用于现实世界自然语言理解任务的示例,请参阅 [SNGP-BERT 教程](https://tensorflow.google.cn/text/tutorials/uncertainty_quantification_with_sngp_bert)。有关基于各种基准数据集(例如 [CIFAR-100](https://tensorflow.google.cn/datasets/catalog/cifar100)、[ImageNet](https://tensorflow.google.cn/datasets/catalog/imagenet2012)、[Jigsaw 恶意检测](https://tensorflow.google.cn/datasets/catalog/wikipedia_toxicity_subtypes)等)的 SNGP 模型(和许多其他不确定性方法)的高质量实现方式,请参阅[不确定性基线](https://github.com/google/uncertainty-baselines){.external} 基准。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "K-tZzAIlvMv_"
},
"source": [
"## 关于 SNGP"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "ysyslHCyvYi-"
},
"source": [
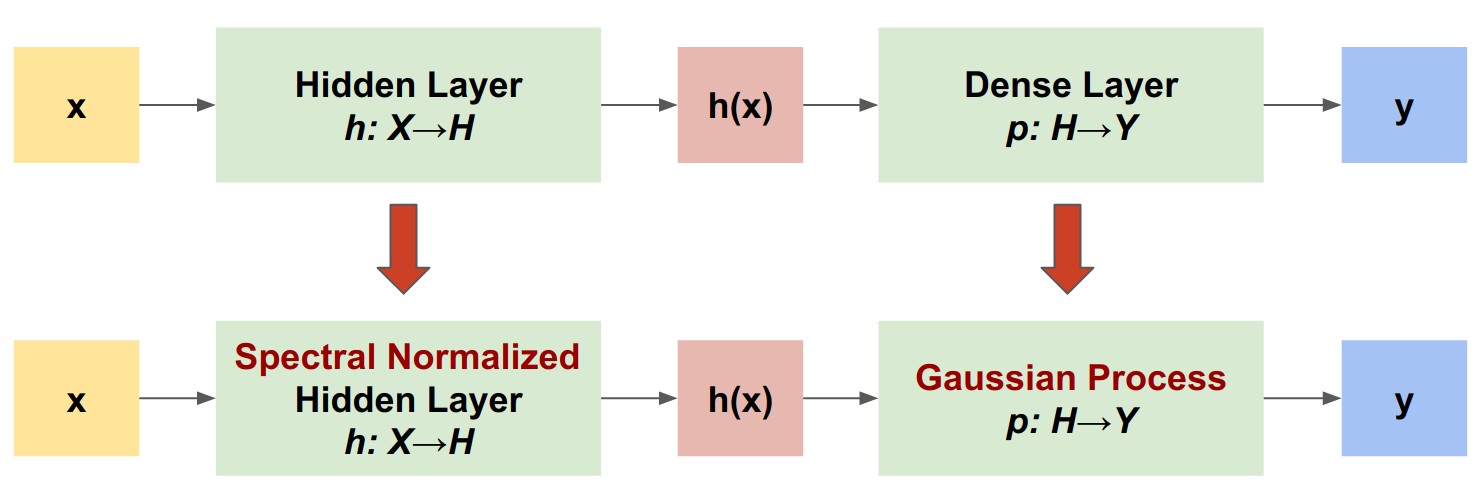
"SNGP 是一种可提高深度分类器的不确定性质量,同时能够保持相似准确率和延迟水平的简单方式。给定一个深度残差网络,SNGP 即会对模型进行两项简单更改:\n",
"\n",
"- 将谱归一化应用于隐藏的残差层。\n",
"- 将 Dense 输出层替换为高斯过程层。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "ffU8rJ_eWHou"
},
"source": [
"> \n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "2L88PoKr6XaE"
},
"source": [
"与其他不确定性方式(例如蒙特卡罗随机失活或深度集成)相比,SNGP 具有以下几项优点:\n",
"\n",
"- 适用于各种最先进的基于残差的架构(例如 (Wide) ResNet、DenseNet 或 BERT)。\n",
"- 是一种单模型方法(不依赖于集合平均)。因此,SNGP 具有与单一确定性网络相似的延迟水平,并且可以轻松扩展至大型数据集,如 [ImageNet](https://github.com/google/uncertainty-baselines/tree/main/baselines/imagenet){.external} 和 [Jigsaw 恶意评论分类](https://github.com/google/uncertainty-baselines/tree/main/baselines/toxic_comments){.external}。\n",
"- *距离感知*属性使之具有强大的域外检测性能。\n",
"\n",
"这种方法的缺点为:\n",
"\n",
"- SNGP 的预测不确定性是使用[拉普拉斯近似](http://www.gaussianprocess.org/gpml/chapters/RW3.pdf){.external}计算的。因此在理论上,SNGP 的后验不确定性与精确高斯过程的后验不确定性不同。\n",
"\n",
"- SNGP 训练需要在新周期开始时进行协方差重置步骤。这会对训练流水线额外增添些许复杂性。本教程展示了一种使用 Keras 回调实现此功能的简单方式。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "ck_O7S8r1boS"
},
"source": [
"## 安装"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "MOS9qFlW2o3J",
"vscode": {
"languageId": "python"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"!pip install -U -q --use-deprecated=legacy-resolver tf-models-official tensorflow"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "RCoGSYz-PIR7",
"vscode": {
"languageId": "python"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# refresh pkg_resources so it takes the changes into account.\n",
"import pkg_resources\n",
"import importlib\n",
"importlib.reload(pkg_resources)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "nJKtMbtYNXHn",
"vscode": {
"languageId": "python"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n",
"import matplotlib.colors as colors\n",
"\n",
"import sklearn.datasets\n",
"\n",
"import numpy as np\n",
"import tensorflow as tf\n",
"\n",
"import official.nlp.modeling.layers as nlp_layers"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "8RCyTrQO4ZXo"
},
"source": [
"定义呈现宏"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "o5VTrcxo3rI-",
"vscode": {
"languageId": "python"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"plt.rcParams['figure.dpi'] = 140\n",
"\n",
"DEFAULT_X_RANGE = (-3.5, 3.5)\n",
"DEFAULT_Y_RANGE = (-2.5, 2.5)\n",
"DEFAULT_CMAP = colors.ListedColormap([\"#377eb8\", \"#ff7f00\"])\n",
"DEFAULT_NORM = colors.Normalize(vmin=0, vmax=1,)\n",
"DEFAULT_N_GRID = 100"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "lL5HzdYT5x5J"
},
"source": [
"## 双月数据集"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "nqazrSzhd24R"
},
"source": [
"从 [scikit-learn 双月数据集](https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.datasets.make_moons.html){.external} 创建训练数据集和评估数据集。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "xJ_ul9Ii52mh",
"vscode": {
"languageId": "python"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"def make_training_data(sample_size=500):\n",
" \"\"\"Create two moon training dataset.\"\"\"\n",
" train_examples, train_labels = sklearn.datasets.make_moons(\n",
" n_samples=2 * sample_size, noise=0.1)\n",
"\n",
" # Adjust data position slightly.\n",
" train_examples[train_labels == 0] += [-0.1, 0.2]\n",
" train_examples[train_labels == 1] += [0.1, -0.2]\n",
"\n",
" return train_examples, train_labels"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "goQkrxR_fFGd"
},
"source": [
"评估模型在整个二维输入空间上的预测行为。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "Cj7ldkNw5-cT",
"vscode": {
"languageId": "python"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"def make_testing_data(x_range=DEFAULT_X_RANGE, y_range=DEFAULT_Y_RANGE, n_grid=DEFAULT_N_GRID):\n",
" \"\"\"Create a mesh grid in 2D space.\"\"\"\n",
" # testing data (mesh grid over data space)\n",
" x = np.linspace(x_range[0], x_range[1], n_grid)\n",
" y = np.linspace(y_range[0], y_range[1], n_grid)\n",
" xv, yv = np.meshgrid(x, y)\n",
" return np.stack([xv.flatten(), yv.flatten()], axis=-1)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "G9BYe4yqfeFa"
},
"source": [
"要评估模型不确定性,请添加属于第三类的域外 (OOD) 数据集。该模型在训练期间从不观测这些 OOD 样本。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "5UHz2SU4feSI",
"vscode": {
"languageId": "python"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"def make_ood_data(sample_size=500, means=(2.5, -1.75), vars=(0.01, 0.01)):\n",
" return np.random.multivariate_normal(\n",
" means, cov=np.diag(vars), size=sample_size)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "l1-jmJb45_at",
"vscode": {
"languageId": "python"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Load the train, test and OOD datasets.\n",
"train_examples, train_labels = make_training_data(\n",
" sample_size=500)\n",
"test_examples = make_testing_data()\n",
"ood_examples = make_ood_data(sample_size=500)\n",
"\n",
"# Visualize\n",
"pos_examples = train_examples[train_labels == 0]\n",
"neg_examples = train_examples[train_labels == 1]\n",
"\n",
"plt.figure(figsize=(7, 5.5))\n",
"\n",
"plt.scatter(pos_examples[:, 0], pos_examples[:, 1], c=\"#377eb8\", alpha=0.5)\n",
"plt.scatter(neg_examples[:, 0], neg_examples[:, 1], c=\"#ff7f00\", alpha=0.5)\n",
"plt.scatter(ood_examples[:, 0], ood_examples[:, 1], c=\"red\", alpha=0.1)\n",
"\n",
"plt.legend([\"Positive\", \"Negative\", \"Out-of-Domain\"])\n",
"\n",
"plt.ylim(DEFAULT_Y_RANGE)\n",
"plt.xlim(DEFAULT_X_RANGE)\n",
"\n",
"plt.show()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "nlzxsnBBkybB"
},
"source": [
"这里,蓝色和橙色代表正负类,红色代表 OOD 数据。能够准确量化不确定性的模型在接近训练数据时(即 $p(x_{test})$ 接近 0 或 1)应达到较高的置信度,而在远离训练数据区域时(即 $p(x_{test})$ 接近 0.5)则不确定性较高。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "RJ3i4n8li-Mv"
},
"source": [
"## 确定性模型"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "Utncgxs3lc4u"
},
"source": [
"### 定义模型"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "-z83-nq6jPlb"
},
"source": [
"从(基线)确定性模型开始:具有随机失活正则化的多层残差网络 (ResNet)。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"cellView": "form",
"id": "wCBRm8fc6CgY",
"vscode": {
"languageId": "python"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"#@title\n",
"class DeepResNet(tf.keras.Model):\n",
" \"\"\"Defines a multi-layer residual network.\"\"\"\n",
" def __init__(self, num_classes, num_layers=3, num_hidden=128,\n",
" dropout_rate=0.1, **classifier_kwargs):\n",
" super().__init__()\n",
" # Defines class meta data.\n",
" self.num_hidden = num_hidden\n",
" self.num_layers = num_layers\n",
" self.dropout_rate = dropout_rate\n",
" self.classifier_kwargs = classifier_kwargs\n",
"\n",
" # Defines the hidden layers.\n",
" self.input_layer = tf.keras.layers.Dense(self.num_hidden, trainable=False)\n",
" self.dense_layers = [self.make_dense_layer() for _ in range(num_layers)]\n",
"\n",
" # Defines the output layer.\n",
" self.classifier = self.make_output_layer(num_classes)\n",
"\n",
" def call(self, inputs):\n",
" # Projects the 2d input data to high dimension.\n",
" hidden = self.input_layer(inputs)\n",
"\n",
" # Computes the ResNet hidden representations.\n",
" for i in range(self.num_layers):\n",
" resid = self.dense_layers[i](hidden)\n",
" resid = tf.keras.layers.Dropout(self.dropout_rate)(resid)\n",
" hidden += resid\n",
"\n",
" return self.classifier(hidden)\n",
"\n",
" def make_dense_layer(self):\n",
" \"\"\"Uses the Dense layer as the hidden layer.\"\"\"\n",
" return tf.keras.layers.Dense(self.num_hidden, activation=\"relu\")\n",
"\n",
" def make_output_layer(self, num_classes):\n",
" \"\"\"Uses the Dense layer as the output layer.\"\"\"\n",
" return tf.keras.layers.Dense(\n",
" num_classes, **self.classifier_kwargs)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "4u870GAen2aO"
},
"source": [
"本教程使用具有 128 个隐藏单元的六层 ResNet。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "bWL9wCnGpc4h",
"vscode": {
"languageId": "python"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"resnet_config = dict(num_classes=2, num_layers=6, num_hidden=128)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "I47RY26wurgg",
"vscode": {
"languageId": "python"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"resnet_model = DeepResNet(**resnet_config)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "okQXf2F1ur16",
"vscode": {
"languageId": "python"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"resnet_model.build((None, 2))\n",
"resnet_model.summary()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "8ZzueLoImW0t"
},
"source": [
"### 训练模型"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "JfQ1k-IUukLt"
},
"source": [
"配置训练参数以使用 `SparseCategoricalCrossentropy` 作为损失函数和 Adam 优化器。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "a9ZkfNXAnumV",
"vscode": {
"languageId": "python"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"loss = tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True)\n",
"metrics = tf.keras.metrics.SparseCategoricalAccuracy(),\n",
"optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.legacy.Adam(learning_rate=1e-4)\n",
"\n",
"train_config = dict(loss=loss, metrics=metrics, optimizer=optimizer)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "wEWzfHvf6A5_"
},
"source": [
"以 128 为批次大小对模型训练 100 个周期。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "1Fx6EtGXpzVr",
"vscode": {
"languageId": "python"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"fit_config = dict(batch_size=128, epochs=100)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "cFwkbKIuqj7Y",
"vscode": {
"languageId": "python"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"resnet_model.compile(**train_config)\n",
"resnet_model.fit(train_examples, train_labels, **fit_config)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "eo6tKKd1rvBh"
},
"source": [
"### 呈现不确定性"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"cellView": "form",
"id": "HZDMX7gZrZ-5",
"vscode": {
"languageId": "python"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"#@title\n",
"def plot_uncertainty_surface(test_uncertainty, ax, cmap=None):\n",
" \"\"\"Visualizes the 2D uncertainty surface.\n",
" \n",
" For simplicity, assume these objects already exist in the memory:\n",
"\n",
" test_examples: Array of test examples, shape (num_test, 2).\n",
" train_labels: Array of train labels, shape (num_train, ).\n",
" train_examples: Array of train examples, shape (num_train, 2).\n",
" \n",
" Arguments:\n",
" test_uncertainty: Array of uncertainty scores, shape (num_test,).\n",
" ax: A matplotlib Axes object that specifies a matplotlib figure.\n",
" cmap: A matplotlib colormap object specifying the palette of the\n",
" predictive surface.\n",
"\n",
" Returns:\n",
" pcm: A matplotlib PathCollection object that contains the palette\n",
" information of the uncertainty plot.\n",
" \"\"\"\n",
" # Normalize uncertainty for better visualization.\n",
" test_uncertainty = test_uncertainty / np.max(test_uncertainty)\n",
"\n",
" # Set view limits.\n",
" ax.set_ylim(DEFAULT_Y_RANGE)\n",
" ax.set_xlim(DEFAULT_X_RANGE)\n",
"\n",
" # Plot normalized uncertainty surface.\n",
" pcm = ax.imshow(\n",
" np.reshape(test_uncertainty, [DEFAULT_N_GRID, DEFAULT_N_GRID]),\n",
" cmap=cmap,\n",
" origin=\"lower\",\n",
" extent=DEFAULT_X_RANGE + DEFAULT_Y_RANGE,\n",
" vmin=DEFAULT_NORM.vmin,\n",
" vmax=DEFAULT_NORM.vmax,\n",
" interpolation='bicubic',\n",
" aspect='auto')\n",
"\n",
" # Plot training data.\n",
" ax.scatter(train_examples[:, 0], train_examples[:, 1],\n",
" c=train_labels, cmap=DEFAULT_CMAP, alpha=0.5)\n",
" ax.scatter(ood_examples[:, 0], ood_examples[:, 1], c=\"red\", alpha=0.1)\n",
"\n",
" return pcm"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "a1age2y0339T"
},
"source": [
"现在,呈现确定性模型的预测。首先绘制类概率:$$p(x) = softmax(logit(x))$$"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "4aqFgQOD40lb",
"vscode": {
"languageId": "python"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"resnet_logits = resnet_model(test_examples)\n",
"resnet_probs = tf.nn.softmax(resnet_logits, axis=-1)[:, 0] # Take the probability for class 0."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "rpflH2Qj33oN",
"vscode": {
"languageId": "python"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"_, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(7, 5.5))\n",
"\n",
"pcm = plot_uncertainty_surface(resnet_probs, ax=ax)\n",
"\n",
"plt.colorbar(pcm, ax=ax)\n",
"plt.title(\"Class Probability, Deterministic Model\")\n",
"\n",
"plt.show()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "7ShGAB7FNYgU"
},
"source": [
"在此图中,黄色和紫色为这两个类的预测概率。确定性模型在利用非线性决策边界对两个已知类(蓝色和橙色)进行分类方面表现优秀。然而,它并不具备**距离感知**,并且会以较高的置信度将从未观测到的红色域外 (OOD) 样本分类为橙色类。\n",
"\n",
"通过计算[预测方差](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bernoulli_distribution#Variance)来呈现模型的不确定性:<code class=\"part_formula\"><code class=\"part_formula\">$$var(x) = p(x) * (1 - p(x))$$"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "VxMce5D15Qwt",
"vscode": {
"languageId": "python"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"resnet_uncertainty = resnet_probs * (1 - resnet_probs)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "fwdEfb5_6woh",
"vscode": {
"languageId": "python"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"_, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(7, 5.5))\n",
"\n",
"pcm = plot_uncertainty_surface(resnet_uncertainty, ax=ax)\n",
"\n",
"plt.colorbar(pcm, ax=ax)\n",
"plt.title(\"Predictive Uncertainty, Deterministic Model\")\n",
"\n",
"plt.show()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "alVunBEXhD-1"
},
"source": [
"在此图中,黄色表示高不确定性,紫色表示低不确定性。确定性 ResNet 的不确定性仅取决于测试样本与决策边界之间的距离。这会导致模型在超出训练域时出现置信度过度的问题。下一部分将展示 SNGP 在此数据集上的行为方式有何不同。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "CwDa80iOh32J"
},
"source": [
"## SNGP 模型"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "IbjNrmLu8oXv"
},
"source": [
"### 定义 SNGP 模型"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "urtuCrk1Hf5P"
},
"source": [
"现在,我们来实现 SNGP 模型。SNGP 组件 `SpectralNormalization` 和 `RandomFeatureGaussianProcess` 均在 tensorflow_model 的[内置层](https://github.com/tensorflow/models/tree/master/official/nlp/modeling/layers)中可用。 "
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "7IlQwKCEGwpk"
},
"source": [
"> \n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "rp2O2iv8LSke"
},
"source": [
"让我们更加详细地检查这两个组件。(您也可以跳转到[完整 SNGP 模型](#full-sngp-model)部分以了解 SNGP 的实现方法。)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "5n4NIt3QjKwl"
},
"source": [
"#### `SpectralNormalization` 封装容器"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "tE-Va7J2jR2X"
},
"source": [
"[`SpectralNormalization`](https://github.com/tensorflow/models/blob/master/official/nlp/modeling/layers/spectral_normalization.py){.external} 是 Keras 层封装容器。它能够以如下方式应用于现有的 Dense 层:"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "Dp8vqJBWLSq3",
"vscode": {
"languageId": "python"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"dense = tf.keras.layers.Dense(units=10)\n",
"dense = nlp_layers.SpectralNormalization(dense, norm_multiplier=0.9)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "E9q25_6fRJRh"
},
"source": [
"谱归一化会通过将其谱范数(即 $W$ 的最大特征值)朝目标值 `norm_multiplier` 逐渐引导来正则化隐藏权重 $W$。\n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "cqt-DVzvqyAE"
},
"source": [
"注:通常情况下,最好将 `norm_multiplier` 设置为小于 1 的值。但在实践中,也可以将其放宽为更大的值,以确保深度网络具有足够的表达力。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "yqvxJUXBjBhV"
},
"source": [
"#### 高斯过程 (GP) 层"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "7rYfIgtrjHnB"
},
"source": [
"[`RandomFeatureGaussianProcess`](https://github.com/tensorflow/models/blob/master/official/nlp/modeling/layers/gaussian_process.py){.external} 可对能够通过深度神经网络进行端到端训练的高斯过程模型实现[基于随机特征的近似](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~brecht/papers/07.rah.rec.nips.pdf){.external}。从底层来看,高斯过程层实现了一个两层网络:\n",
"\n",
"```\n",
"$$logits(x) = \\Phi(x) \\beta, \\quad \\Phi(x)=\\sqrt{\\frac{2}{M}} * cos(Wx + b)$$\n",
"```\n",
"\n",
"Here, $x$ is the input, and $W$ and $b$ are frozen weights initialized randomly from Gaussian and Uniform distributions, respectively. (Therefore, $\\Phi(x)$ are called \"random features\".) $\\beta$ is the learnable kernel weight similar to that of a Dense layer. "
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "NqnU39ui3wAE",
"vscode": {
"languageId": "python"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"batch_size = 32\n",
"input_dim = 1024\n",
"num_classes = 10"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "LrlVd-foRJno",
"vscode": {
"languageId": "python"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"gp_layer = nlp_layers.RandomFeatureGaussianProcess(units=num_classes,\n",
" num_inducing=1024,\n",
" normalize_input=False,\n",
" scale_random_features=True,\n",
" gp_cov_momentum=-1)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "xxb8sSAg5AGf"
},
"source": [
"GP 层的主要参数包括:\n",
"\n",
"- `units`:输出 logit 的维度。\n",
"- `num_inducing`:隐藏权重 $W$ 的维度 $M$。默认值为 1024。\n",
"- `normalize_input`:是否对输入 $x$ 应用层归一化。\n",
"- `scale_random_features`:是否将缩放 $\\sqrt{2/M}$ 应用于隐藏输出。\n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "xgzw09gS03ae"
},
"source": [
"注:对于对学习率较为敏感的深度神经网络(例如 ResNet-50 和 ResNet-110),一般建议设置 `normalize_input=True` 以提高训练稳定性,并设置 `scale_random_features=False` 以避免在通过 GP 层时学习率被意外修改。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "pZkcKw-u7XRp"
},
"source": [
"- `gp_cov_momentum` 可以控制如何计算模型协方差。如果设置为正值(例如 `0.999`),将使用基于动量的移动平均值更新(类似于批归一化)计算协方差矩阵。如果设置为 `-1`,则协方差矩阵将在无动量情况下更新。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "P13X7Adt-c2d"
},
"source": [
"注:基于动量的更新方法可能会对批次大小较为敏感。因此,通常建议设置 `gp_cov_momentum=-1` 以精确计算协方差。为了使其正常工作,协方差矩阵 estimator 需要在新周期开始时重置,以避免重复计算相同的数据。对于 `RandomFeatureGaussianProcess`,这可以通过调用其 `reset_covariance_matrix()` 来实现。下一部分展示了使用 Keras 内置 API 的简单实现。\n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "0AA492qA1biZ"
},
"source": [
"给定一个形状为 `(batch_size, input_dim)` 的批次输入,GP 层会返回 `logits` 张量(形状为 `(batch_size, num_classes)`)用于预测;以及 `covmat` 张量(形状为 `(batch_size, batch_size)`),它是批次 logit 的后验协方差矩阵。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "yOXxBYnMi1v4",
"vscode": {
"languageId": "python"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"embedding = tf.random.normal(shape=(batch_size, input_dim))\n",
"\n",
"logits, covmat = gp_layer(embedding)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "ALBqcAtwDNiO"
},
"source": [
"注:请注意,在 SNGP 模型的这种实现方式下,所有类的预测 logit $logit(x_{test})$ 都会共享相同的协方差矩阵 $var(x_{test})$,后者描述了 $x_{test}$ 与训练数据之间的距离。\n",
"\n",
"理论上讲,可以扩展算法来为不同类计算不同的方差值(如[原始 SNGP 论文](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.10108){.external}中所介绍)。但是,这很难扩展到具有大输出空间的问题(例如使用 ImageNet 或语言建模的分类)。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "II3GVzjJhu5Z"
},
"source": [
"\n",
"\n",
"#### 完整 SNGP 模型"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "F5Fm0NUlLTHd"
},
"source": [
"给定基类 `DeepResNet`,即可通过修改残差网络的隐藏层和输出层来轻松实现 SNGP 模型。为了与 Keras `model.fit()` API 兼容,还需修改模型的 `call()` 方法,使其仅在训练期间输出 `logits`。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "Dzx4FsO97QZv",
"vscode": {
"languageId": "python"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"class DeepResNetSNGP(DeepResNet):\n",
" def __init__(self, spec_norm_bound=0.9, **kwargs):\n",
" self.spec_norm_bound = spec_norm_bound\n",
" super().__init__(**kwargs)\n",
"\n",
" def make_dense_layer(self):\n",
" \"\"\"Applies spectral normalization to the hidden layer.\"\"\"\n",
" dense_layer = super().make_dense_layer()\n",
" return nlp_layers.SpectralNormalization(\n",
" dense_layer, norm_multiplier=self.spec_norm_bound)\n",
"\n",
" def make_output_layer(self, num_classes):\n",
" \"\"\"Uses Gaussian process as the output layer.\"\"\"\n",
" return nlp_layers.RandomFeatureGaussianProcess(\n",
" num_classes,\n",
" gp_cov_momentum=-1,\n",
" **self.classifier_kwargs)\n",
"\n",
" def call(self, inputs, training=False, return_covmat=False):\n",
" # Gets logits and a covariance matrix from the GP layer.\n",
" logits, covmat = super().call(inputs)\n",
"\n",
" # Returns only logits during training.\n",
" if not training and return_covmat:\n",
" return logits, covmat\n",
"\n",
" return logits"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "02SvlnDFyszm"
},
"source": [
"使用与确定性模型相同的架构。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "QiDcC5ipyqMU",
"vscode": {
"languageId": "python"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"resnet_config"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "D9-imQtDyZL5",
"vscode": {
"languageId": "python"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"sngp_model = DeepResNetSNGP(**resnet_config)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "12P9UxlCyq6k",
"vscode": {
"languageId": "python"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"sngp_model.build((None, 2))\n",
"sngp_model.summary()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "BlCgMRrwkXgN"
},
"source": [
" 实现 Keras 回调以在新周期开始时重置协方差矩阵。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "W6Wr8D_0n-cQ",
"vscode": {
"languageId": "python"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"class ResetCovarianceCallback(tf.keras.callbacks.Callback):\n",
"\n",
" def on_epoch_begin(self, epoch, logs=None):\n",
" \"\"\"Resets covariance matrix at the beginning of the epoch.\"\"\"\n",
" if epoch > 0:\n",
" self.model.classifier.reset_covariance_matrix()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "NMiz_mYawEPh"
},
"source": [
"将此回调添加到 `DeepResNetSNGP` 模型类。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "yrSi0ZD5zaDf",
"vscode": {
"languageId": "python"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"class DeepResNetSNGPWithCovReset(DeepResNetSNGP):\n",
" def fit(self, *args, **kwargs):\n",
" \"\"\"Adds ResetCovarianceCallback to model callbacks.\"\"\"\n",
" kwargs[\"callbacks\"] = list(kwargs.get(\"callbacks\", []))\n",
" kwargs[\"callbacks\"].append(ResetCovarianceCallback())\n",
"\n",
" return super().fit(*args, **kwargs)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "asIwYqGlwJcP"
},
"source": [
"### 训练模型"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "4YRzayOCopt9"
},
"source": [
"使用 `tf.keras.model.fit` 训练模型。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "coazo53nwJqv",
"vscode": {
"languageId": "python"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"sngp_model = DeepResNetSNGPWithCovReset(**resnet_config)\n",
"sngp_model.compile(**train_config)\n",
"sngp_model.fit(train_examples, train_labels, **fit_config)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "KTONd8vowgEP"
},
"source": [
"### 呈现不确定性"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "yhkpsiy10l9d"
},
"source": [
"首先,计算预测 logit 和方差。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "bqRPqeEavi4Z",
"vscode": {
"languageId": "python"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"sngp_logits, sngp_covmat = sngp_model(test_examples, return_covmat=True)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "p7w0iW_L0cU8",
"vscode": {
"languageId": "python"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"sngp_variance = tf.linalg.diag_part(sngp_covmat)[:, None]"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "YLbz_EZF1Gay"
},
"source": [
" 现在,计算后验预测概率。计算概率模型预测概率的经典方法是使用蒙特卡罗采样法,即:\n",
"\n",
"```\n",
"$$E(p(x)) = \\frac{1}{M} \\sum_{m=1}^M logit_m(x), $$\n",
"```\n",
"\n",
"其中 $M$ 为样本大小,$logit_m(x)$ 为来自 SNGP 后验 $MultivariateNormal$(`sngp_logits`,`sngp_covmat`) 的随机样本。但是,这种方式对于延迟敏感型应用(例如自动驾驶或实时竞价)而言,速度可能较慢。相反,您可以使用[平均场法](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.07584){.external}来逼近 $E(p(x))$:\n",
"\n",
"```\n",
"$$E(p(x)) \\approx softmax(\\frac{logit(x)}{\\sqrt{1+ \\lambda * \\sigma^2(x)}})$$\n",
"```\n",
"\n",
"where $\\sigma^2(x)$ is the SNGP variance, and $\\lambda$ is often chosen as $\\pi/8$ or $3/\\pi^2$."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "1A9NYMhd0iZ-",
"vscode": {
"languageId": "python"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"sngp_logits_adjusted = sngp_logits / tf.sqrt(1. + (np.pi / 8.) * sngp_variance)\n",
"sngp_probs = tf.nn.softmax(sngp_logits_adjusted, axis=-1)[:, 0]"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "bNVs_KO-5HdL"
},
"source": [
"注:除了将 $\\lambda$ 限定为固定值之外,您还可以将其视为超参数,并对其进行调整以优化模型的校准性能。这在深度学习不确定性文献中被称为[温度缩放](http://proceedings.mlr.press/v70/guo17a.html){.external}。 "
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "DlYPlUbJfBFa"
},
"source": [
"这种平均场方法以内置函数 `layers.gaussian_process.mean_field_logits` 形式实现:"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "hgb3WSaY8iQY",
"vscode": {
"languageId": "python"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"def compute_posterior_mean_probability(logits, covmat, lambda_param=np.pi / 8.):\n",
" # Computes uncertainty-adjusted logits using the built-in method.\n",
" logits_adjusted = nlp_layers.gaussian_process.mean_field_logits(\n",
" logits, covmat, mean_field_factor=lambda_param)\n",
" \n",
" return tf.nn.softmax(logits_adjusted, axis=-1)[:, 0]"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "kVToZpG7QqS3",
"vscode": {
"languageId": "python"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"sngp_logits, sngp_covmat = sngp_model(test_examples, return_covmat=True)\n",
"sngp_probs = compute_posterior_mean_probability(sngp_logits, sngp_covmat)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "bVi_Whpwe3O4"
},
"source": [
"### SNGP 摘要"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"cellView": "form",
"id": "dRmmxuO41BV4",
"vscode": {
"languageId": "python"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"#@title\n",
"\n",
"def plot_predictions(pred_probs, model_name=\"\"):\n",
" \"\"\"Plot normalized class probabilities and predictive uncertainties.\"\"\"\n",
" # Compute predictive uncertainty.\n",
" uncertainty = pred_probs * (1. - pred_probs)\n",
"\n",
" # Initialize the plot axes.\n",
" fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(14, 5))\n",
"\n",
" # Plots the class probability.\n",
" pcm_0 = plot_uncertainty_surface(pred_probs, ax=axs[0])\n",
" # Plots the predictive uncertainty.\n",
" pcm_1 = plot_uncertainty_surface(uncertainty, ax=axs[1])\n",
"\n",
" # Adds color bars and titles.\n",
" fig.colorbar(pcm_0, ax=axs[0])\n",
" fig.colorbar(pcm_1, ax=axs[1])\n",
"\n",
" axs[0].set_title(f\"Class Probability, {model_name}\")\n",
" axs[1].set_title(f\"(Normalized) Predictive Uncertainty, {model_name}\")\n",
"\n",
" plt.show() "
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "R9kY5dJg8fEi"
},
"source": [
"您现在可以将所有内容归总到一起。整个过程(训练、评估和不确定性计算)只需五行即可完成:"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "NQtUAG4-ftqe",
"vscode": {
"languageId": "python"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"def train_and_test_sngp(train_examples, test_examples):\n",
" sngp_model = DeepResNetSNGPWithCovReset(**resnet_config)\n",
"\n",
" sngp_model.compile(**train_config)\n",
" sngp_model.fit(train_examples, train_labels, verbose=0, **fit_config)\n",
"\n",
" sngp_logits, sngp_covmat = sngp_model(test_examples, return_covmat=True)\n",
" sngp_probs = compute_posterior_mean_probability(sngp_logits, sngp_covmat)\n",
"\n",
" return sngp_probs"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "Dl3N7kHJ283w",
"vscode": {
"languageId": "python"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"sngp_probs = train_and_test_sngp(train_examples, test_examples)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "OAUGrXSv6k3R"
},
"source": [
"呈现 SNGP 模型的类概率(左)和预测不确定性(右)。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "rxt3CY51A_jq",
"vscode": {
"languageId": "python"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"plot_predictions(sngp_probs, model_name=\"SNGP\")"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "raHP5Vuiuku9"
},
"source": [
"请记住,在类概率图(左)中,黄色和紫色为类概率。当接近训练数据域时,SNGP 会以较高的置信度正确分类样本(即,分配接近 0 或 1 的概率)。当远离训练数据时,SNGP 的置信度会逐渐下降,其预测概率接近 0.5,而(归一化)模型不确定性上升到 1。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "u4_VRi9w7Km3"
},
"source": [
"将此与确定性模型的不确定性表面进行比较: "
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "aMAdstYZ7T_w",
"vscode": {
"languageId": "python"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"plot_predictions(resnet_probs, model_name=\"Deterministic\")"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "mao9L-LYE1Nl"
},
"source": [
"如上文所述,确定性模型不具备*距离感知*。它的不确定性会由测试样本与决策边界之间的距离定义。这会导致模型对域外样本(红色)产生置信度过高的预测。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "EKURpzOf0oNq"
},
"source": [
"## 与其他不确定性方式的比较"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "S1DPELWE6LL8"
},
"source": [
"本部分将对 SNGP 的不确定性与[蒙特卡罗随机失活](https://arxiv.org/abs/1506.02142){.external}和[深度集成](https://arxiv.org/abs/1612.01474){.external}进行比较。\n",
"\n",
"这两种方法均基于确定性模型多个前向传递的蒙特卡罗平均算法。首先,设置集合大小 $M$。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "xLqkihbk8Dey",
"vscode": {
"languageId": "python"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"num_ensemble = 10"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "jM5AQmtIAatd"
},
"source": [
"### 蒙特卡罗随机失活"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "ZBzp2LBt7-kj"
},
"source": [
"给定具有随机失活层的经训练的神经网络,蒙特卡罗随机失活会计算平均预测概率\n",
"\n",
"```\n",
"$$E(p(x)) = \\frac{1}{M}\\sum_{m=1}^M softmax(logit_m(x))$$\n",
"```\n",
"\n",
"方法是对多个启用随机失活的前向传递求平均值 ${logit_m(x)}_{m=1}^M$。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "I7R2WBgq4-OC",
"vscode": {
"languageId": "python"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"def mc_dropout_sampling(test_examples):\n",
" # Enable dropout during inference.\n",
" return resnet_model(test_examples, training=True)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "r6oXgaDZAiD0",
"vscode": {
"languageId": "python"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Monte Carlo dropout inference.\n",
"dropout_logit_samples = [mc_dropout_sampling(test_examples) for _ in range(num_ensemble)]\n",
"dropout_prob_samples = [tf.nn.softmax(dropout_logits, axis=-1)[:, 0] for dropout_logits in dropout_logit_samples]\n",
"dropout_probs = tf.reduce_mean(dropout_prob_samples, axis=0)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "_oUNtbVG-YuI",
"vscode": {
"languageId": "python"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"dropout_probs = tf.reduce_mean(dropout_prob_samples, axis=0)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "J-mhyp8hAiPn",
"vscode": {
"languageId": "python"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"plot_predictions(dropout_probs, model_name=\"MC Dropout\")"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "mwtj2vTB75cF"
},
"source": [
"### 深度集成"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "L-Z2veGJ9ZgY"
},
"source": [
"深度集成是一种用于深度学习不确定性的最先进(但耗费算力)的方法。要训练深度集成,首先需要训练 $M$ 个集合成员。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "a43hxiJC3Kla",
"vscode": {
"languageId": "python"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Deep ensemble training\n",
"resnet_ensemble = []\n",
"for _ in range(num_ensemble):\n",
" resnet_model = DeepResNet(**resnet_config)\n",
" resnet_model.compile(optimizer=optimizer, loss=loss, metrics=metrics)\n",
" resnet_model.fit(train_examples, train_labels, verbose=0, **fit_config)\n",
"\n",
" resnet_ensemble.append(resnet_model)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "Al7uM-fn_ZE1"
},
"source": [
"收集 logit 并计算平均预测概率 $E(p(x)) = \\frac{1}{M}\\sum_{m=1}^M softmax(logit_m(x))$。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "c6E9PntV3Mue",
"vscode": {
"languageId": "python"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Deep ensemble inference\n",
"ensemble_logit_samples = [model(test_examples) for model in resnet_ensemble]\n",
"ensemble_prob_samples = [tf.nn.softmax(logits, axis=-1)[:, 0] for logits in ensemble_logit_samples]\n",
"ensemble_probs = tf.reduce_mean(ensemble_prob_samples, axis=0)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "Z_JhYftG-NKR",
"vscode": {
"languageId": "python"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"plot_predictions(ensemble_probs, model_name=\"Deep ensemble\")"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "GH33oVvV5-ez"
},
"source": [
"蒙特卡罗随机失活和深度集成方法都会通过降低决策边界的确定性来提高模型的不确定性能力。然而,二者均继承了确定性深度网络在缺乏距离感知方面的局限性。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "x9nAaWuYfD03"
},
"source": [
"## 总结"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "-ryMkRllFHOC"
},
"source": [
"在本教程中,您已:\n",
"\n",
"- 在深度分类器上实现了 SNGP 模型以提高其距离感知能力。\n",
"- 使用 Keras `Model.fit` API 端到端地训练了 SNGP 模型。\n",
"- 呈现了 SNGP 的不确定性行为。\n",
"- 比较了 SNGP、蒙特卡罗随机失活和深度集成模型之间的不确定性行为。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "UoTekiQmkZXF"
},
"source": [
"## 资源和延伸阅读"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "HoIikRybke-b"
},
"source": [
"- 请参阅 [SNGP-BERT 教程](https://tensorflow.google.cn/text/tutorials/uncertainty_quantification_with_sngp_bert)以查看在 BERT 模型上应用 SNGP 以实现不确定性感知型自然语言理解的示例。\n",
"- 请转到[不确定性基线 GitHub 仓库](https://github.com/google/uncertainty-baselines){.external}以查看在各种基准数据集(例如,[CIFAR](https://tensorflow.google.cn/datasets/catalog/cifar100)、[ImageNet](https://tensorflow.google.cn/datasets/catalog/imagenet2012)、[Jigsaw 恶意检测](https://tensorflow.google.cn/datasets/catalog/wikipedia_toxicity_subtypes)等)上实现 SNGP 模型(和许多其他不确定性方法)的方式。\n",
"- 如需更深入地了解 SNGP 方法,请参阅题为 [Simple and Principled Uncertainty Estimation with Deterministic Deep Learning via Distance Awareness](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.10108){.external} 的论文。\n"
]
}
],
"metadata": {
"colab": {
"collapsed_sections": [],
"name": "sngp.ipynb",
"toc_visible": true
},
"kernelspec": {
"display_name": "Python 3",
"name": "python3"
}
},
"nbformat": 4,
"nbformat_minor": 0
}
 在 TensorFlow.org 上查看
在 TensorFlow.org 上查看  在 Google Colab 中运行
在 Google Colab 中运行  在 GitHub 上查看源代码
在 GitHub 上查看源代码  下载笔记本
下载笔记本  在 TensorFlow.org 上查看
在 TensorFlow.org 上查看  在 Google Colab 中运行
在 Google Colab 中运行  在 GitHub 上查看源代码
在 GitHub 上查看源代码  下载笔记本
下载笔记本