{
"cells": [
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"cellView": "form",
"id": "tXAbWHtqs1Y2"
},
"source": [
"````{admonition} Copyright 2018 The TensorFlow Authors.\n",
"```\n",
"#@title Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the \"License\");\n",
"# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.\n",
"# You may obtain a copy of the License at\n",
"#\n",
"# https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0\n",
"#\n",
"# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software\n",
"# distributed under the License is distributed on an \"AS IS\" BASIS,\n",
"# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.\n",
"# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and\n",
"# limitations under the License.\n",
"```\n",
"````"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "HTgMAvQq-PU_"
},
"source": [
"# 不规则张量\n",
"\n",
""
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "5DP8XNP-6zlu"
},
"source": [
"**API 文档:** [`tf.RaggedTensor`](https://tensorflow.google.cn/api_docs/python/tf/RaggedTensor) [`tf.ragged`](https://tensorflow.google.cn/api_docs/python/tf/ragged)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "cDIUjj07-rQg"
},
"source": [
"## 设置"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 1,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"from set_env import temp_dir"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 2,
"metadata": {
"id": "KKvdSorS-pDD"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# !pip install --pre -U tensorflow\n",
"import math\n",
"import tensorflow as tf"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "pxi0m_yf-te5"
},
"source": [
"## 概述\n",
"\n",
"数据有多种形状;张量也应当有多种形状。*不规则张量*是嵌套的可变长度列表的 TensorFlow 等效项。它们使存储和处理包含非均匀形状的数据变得容易,包括:\n",
"\n",
"- 可变长度特征,例如电影的演员名单。\n",
"- 成批的可变长度顺序输入,例如句子或视频剪辑。\n",
"- 分层输入,例如细分为节、段落、句子和单词的文本文档。\n",
"- 结构化输入中的各个字段,例如协议缓冲区。\n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "1mhU_qY3_mla"
},
"source": [
"### 不规则张量的功能\n",
"\n",
"超过一百种 TensorFlow 运算支持不规则张量,包括数学运算(如 `tf.add` 和 `tf.reduce_mean`)、数组运算(如 `tf.concat` 和 `tf.tile`)、字符串操作运算(如 `tf.substr`)、控制流运算(如 `tf.while_loop` 和 `tf.map_fn`)等:"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 3,
"metadata": {
"id": "vGmJGSf_-PVB"
},
"outputs": [
{
"name": "stdout",
"output_type": "stream",
"text": [
"\n",
"tf.Tensor([2.25 nan 5.33333333 6. nan], shape=(5,), dtype=float64)\n",
"\n",
"\n",
"\n",
"\n"
]
}
],
"source": [
"digits = tf.ragged.constant([[3, 1, 4, 1], [], [5, 9, 2], [6], []])\n",
"words = tf.ragged.constant([[\"So\", \"long\"], [\"thanks\", \"for\", \"all\", \"the\", \"fish\"]])\n",
"print(tf.add(digits, 3))\n",
"print(tf.reduce_mean(digits, axis=1))\n",
"print(tf.concat([digits, [[5, 3]]], axis=0))\n",
"print(tf.tile(digits, [1, 2]))\n",
"print(tf.strings.substr(words, 0, 2))\n",
"print(tf.map_fn(tf.math.square, digits))"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "Pt-5OIc8-PVG"
},
"source": [
"还有专门针对不规则张量的方法和运算,包括工厂方法、转换方法和值映射运算。有关支持的运算列表,请参阅 **`tf.ragged` 包文档**。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "r8fjGgf3B_6z"
},
"source": [
"许多 TensorFlow API 都支持不规则张量,包括 [Keras](https://tensorflow.google.cn/guide/keras)、[Dataset](https://tensorflow.google.cn/guide/data)、[tf.function](https://tensorflow.google.cn/guide/function)、[SavedModel](https://tensorflow.google.cn/guide/saved_model) 和 [tf.Example](https://tensorflow.google.cn/tutorials/load_data/tfrecord)。有关详情,请参阅下面的 **TensorFlow API** 部分。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "aTXLjQlcHP8a"
},
"source": [
"与普通张量一样,您可以使用 Python 风格的索引来访问不规则张量的特定切片。有关详情,请参阅下面的**索引**部分。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 4,
"metadata": {
"id": "n8YMKXpI-PVH"
},
"outputs": [
{
"name": "stdout",
"output_type": "stream",
"text": [
"tf.Tensor([3 1 4 1], shape=(4,), dtype=int32)\n"
]
}
],
"source": [
"print(digits[0]) # First row"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 5,
"metadata": {
"id": "Awi8i9q5_DuX"
},
"outputs": [
{
"name": "stdout",
"output_type": "stream",
"text": [
"\n"
]
}
],
"source": [
"print(digits[:, :2]) # First two values in each row."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 6,
"metadata": {
"id": "sXgQtTcgHHMR"
},
"outputs": [
{
"name": "stdout",
"output_type": "stream",
"text": [
"\n"
]
}
],
"source": [
"print(digits[:, -2:]) # Last two values in each row."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "6FU5T_-8-PVK"
},
"source": [
"与普通张量一样,您可以使用 Python 算术和比较运算符来执行逐元素运算。有关详情,请参阅下面的**重载运算符**部分。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 7,
"metadata": {
"id": "2tdUEtb7-PVL"
},
"outputs": [
{
"name": "stdout",
"output_type": "stream",
"text": [
"\n"
]
}
],
"source": [
"print(digits + 3)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 8,
"metadata": {
"id": "X-bxG0nc_Nmf"
},
"outputs": [
{
"name": "stdout",
"output_type": "stream",
"text": [
"\n"
]
}
],
"source": [
"print(digits + tf.ragged.constant([[1, 2, 3, 4], [], [5, 6, 7], [8], []]))"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "2tsw8mN0ESIT"
},
"source": [
"如果需要对 `RaggedTensor` 的值进行逐元素转换,您可以使用 `tf.ragged.map_flat_values`(它采用一个函数加上一个或多个参数的形式),并应用这个函数来转换 `RaggedTensor` 的值。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 9,
"metadata": {
"id": "pvt5URbdEt-D"
},
"outputs": [
{
"name": "stdout",
"output_type": "stream",
"text": [
"\n"
]
}
],
"source": [
"times_two_plus_one = lambda x: x * 2 + 1\n",
"print(tf.ragged.map_flat_values(times_two_plus_one, digits))"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "HNxF6_QKAzkl"
},
"source": [
"不规则张量可以转换为嵌套的 Python `list` 和 NumPy `array`:"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 10,
"metadata": {
"id": "A5NHb8ViA9dt"
},
"outputs": [
{
"data": {
"text/plain": [
"[[3, 1, 4, 1], [], [5, 9, 2], [6], []]"
]
},
"execution_count": 10,
"metadata": {},
"output_type": "execute_result"
}
],
"source": [
"digits.to_list()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 11,
"metadata": {
"id": "2o1wogVyA6Yp"
},
"outputs": [
{
"data": {
"text/plain": [
"array([array([3, 1, 4, 1], dtype=int32), array([], dtype=int32),\n",
" array([5, 9, 2], dtype=int32), array([6], dtype=int32),\n",
" array([], dtype=int32)], dtype=object)"
]
},
"execution_count": 11,
"metadata": {},
"output_type": "execute_result"
}
],
"source": [
"digits.numpy()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "7M5RHOgp-PVN"
},
"source": [
"### 构造不规则张量\n",
"\n",
"构造不规则张量的最简单方式是使用 `tf.ragged.constant`,它会构建与给定的嵌套 Python `list` 或 NumPy `array` 相对应的 `RaggedTensor`:"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 12,
"metadata": {
"id": "yhgKMozw-PVP"
},
"outputs": [
{
"name": "stdout",
"output_type": "stream",
"text": [
"\n"
]
}
],
"source": [
"sentences = tf.ragged.constant([\n",
" [\"Let's\", \"build\", \"some\", \"ragged\", \"tensors\", \"!\"],\n",
" [\"We\", \"can\", \"use\", \"tf.ragged.constant\", \".\"]])\n",
"print(sentences)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 13,
"metadata": {
"id": "TW1g7eE2ee8M"
},
"outputs": [
{
"name": "stdout",
"output_type": "stream",
"text": [
"\n"
]
}
],
"source": [
"paragraphs = tf.ragged.constant([\n",
" [['I', 'have', 'a', 'cat'], ['His', 'name', 'is', 'Mat']],\n",
" [['Do', 'you', 'want', 'to', 'come', 'visit'], [\"I'm\", 'free', 'tomorrow']],\n",
"])\n",
"print(paragraphs)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "SPLn5xHn-PVR"
},
"source": [
"还可以通过将扁平的*值*张量与*行分区*张量进行配对来构造不规则张量,行分区张量使用 `tf.RaggedTensor.from_value_rowids`、`tf.RaggedTensor.from_row_lengths` 和 `tf.RaggedTensor.from_row_splits` 等工厂类方法指示如何将值分成各行。\n",
"\n",
"#### `tf.RaggedTensor.from_value_rowids`\n",
"\n",
"如果您知道每个值属于哪一行,可以使用 `value_rowids` 行分区张量构建 `RaggedTensor`:\n",
"\n",
"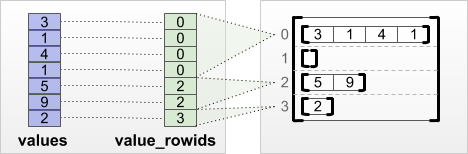"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 14,
"metadata": {
"id": "SEvcPUcl-PVS"
},
"outputs": [
{
"name": "stdout",
"output_type": "stream",
"text": [
"\n"
]
}
],
"source": [
"print(tf.RaggedTensor.from_value_rowids(\n",
" values=[3, 1, 4, 1, 5, 9, 2],\n",
" value_rowids=[0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 2, 3]))"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "RBQh8sYc-PVV"
},
"source": [
"#### `tf.RaggedTensor.from_row_lengths`\n",
"\n",
"如果知道每行的长度,可以使用 `row_lengths` 行分区张量:\n",
"\n",
"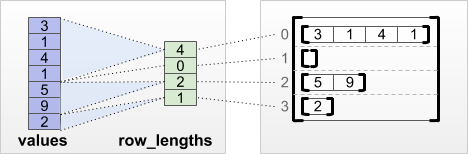"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 15,
"metadata": {
"id": "LBY81WXl-PVW"
},
"outputs": [
{
"name": "stdout",
"output_type": "stream",
"text": [
"\n"
]
}
],
"source": [
"print(tf.RaggedTensor.from_row_lengths(\n",
" values=[3, 1, 4, 1, 5, 9, 2],\n",
" row_lengths=[4, 0, 2, 1]))"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "8p5V8_Iu-PVa"
},
"source": [
"#### `tf.RaggedTensor.from_row_splits`\n",
"\n",
"如果知道指示每行开始和结束的索引,可以使用 `row_splits` 行分区张量:\n",
"\n",
"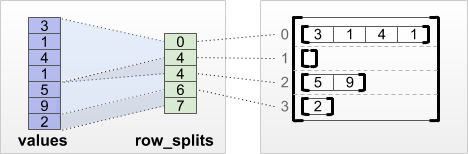"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 16,
"metadata": {
"id": "FwizuqZI-PVb"
},
"outputs": [
{
"name": "stdout",
"output_type": "stream",
"text": [
"\n"
]
}
],
"source": [
"print(tf.RaggedTensor.from_row_splits(\n",
" values=[3, 1, 4, 1, 5, 9, 2],\n",
" row_splits=[0, 4, 4, 6, 7]))"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "E-9imo8DhwuA"
},
"source": [
"有关完整的工厂方法列表,请参阅 `tf.RaggedTensor` 类文档。\n",
"\n",
"注:默认情况下,这些工厂方法会添加断言,说明行分区张量结构良好且与值数量保持一致。如果您能够保证输入的结构良好且一致,可以使用 `validate=False` 参数跳过此类检查。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "YQAOsT1_-PVg"
},
"source": [
"### 可以在不规则张量中存储什么\n",
"\n",
"与普通 `Tensor` 一样,`RaggedTensor` 中的所有值必须具有相同的类型;所有值必须处于相同的嵌套深度(张量的*秩*):"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 17,
"metadata": {
"id": "SqbPBd_w-PVi"
},
"outputs": [
{
"name": "stdout",
"output_type": "stream",
"text": [
"\n"
]
}
],
"source": [
"print(tf.ragged.constant([[\"Hi\"], [\"How\", \"are\", \"you\"]])) # ok: type=string, rank=2"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 18,
"metadata": {
"id": "83ZCSJnQAWAf"
},
"outputs": [
{
"name": "stdout",
"output_type": "stream",
"text": [
"\n"
]
}
],
"source": [
"print(tf.ragged.constant([[[1, 2], [3]], [[4, 5]]])) # ok: type=int32, rank=3"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 19,
"metadata": {
"id": "ewA3cISdDfmP"
},
"outputs": [
{
"name": "stdout",
"output_type": "stream",
"text": [
"Can't convert Python sequence with mixed types to Tensor.\n"
]
}
],
"source": [
"try:\n",
" tf.ragged.constant([[\"one\", \"two\"], [3, 4]]) # bad: multiple types\n",
"except ValueError as exception:\n",
" print(exception)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 20,
"metadata": {
"id": "EOWIlVidDl-n"
},
"outputs": [
{
"name": "stdout",
"output_type": "stream",
"text": [
"all scalar values must have the same nesting depth\n"
]
}
],
"source": [
"try:\n",
" tf.ragged.constant([\"A\", [\"B\", \"C\"]]) # bad: multiple nesting depths\n",
"except ValueError as exception:\n",
" print(exception)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "nhHMFhSp-PVq"
},
"source": [
"## 示例用例\n",
"\n",
"以下示例演示了如何使用 `RaggedTensor`,通过为每个句子的开头和结尾使用特殊标记,为一批可变长度查询构造和组合一元与二元嵌入向量。有关本例中使用的运算的更多详细信息,请参阅 `tf.ragged` 软件包文档。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 21,
"metadata": {
"id": "ZBs_V7e--PVr"
},
"outputs": [
{
"name": "stdout",
"output_type": "stream",
"text": [
"tf.Tensor(\n",
"[[-0.28740856 0.02230661 -0.1435088 0.03474583]\n",
" [ 0.10811251 -0.26461127 0.15405743 -0.27250707]\n",
" [-0.04733209 0.11316853 -0.46375054 0.14681712]], shape=(3, 4), dtype=float32)\n"
]
}
],
"source": [
"queries = tf.ragged.constant([['Who', 'is', 'Dan', 'Smith'],\n",
" ['Pause'],\n",
" ['Will', 'it', 'rain', 'later', 'today']])\n",
"\n",
"# Create an embedding table.\n",
"num_buckets = 1024\n",
"embedding_size = 4\n",
"embedding_table = tf.Variable(\n",
" tf.random.truncated_normal([num_buckets, embedding_size],\n",
" stddev=1.0 / math.sqrt(embedding_size)))\n",
"\n",
"# Look up the embedding for each word.\n",
"word_buckets = tf.strings.to_hash_bucket_fast(queries, num_buckets)\n",
"word_embeddings = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(embedding_table, word_buckets) # ①\n",
"\n",
"# Add markers to the beginning and end of each sentence.\n",
"marker = tf.fill([queries.nrows(), 1], '#')\n",
"padded = tf.concat([marker, queries, marker], axis=1) # ②\n",
"\n",
"# Build word bigrams and look up embeddings.\n",
"bigrams = tf.strings.join([padded[:, :-1], padded[:, 1:]], separator='+') # ③\n",
"\n",
"bigram_buckets = tf.strings.to_hash_bucket_fast(bigrams, num_buckets)\n",
"bigram_embeddings = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(embedding_table, bigram_buckets) # ④\n",
"\n",
"# Find the average embedding for each sentence\n",
"all_embeddings = tf.concat([word_embeddings, bigram_embeddings], axis=1) # ⑤\n",
"avg_embedding = tf.reduce_mean(all_embeddings, axis=1) # ⑥\n",
"print(avg_embedding)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "Y_lE_LAVcWQH"
},
"source": [
"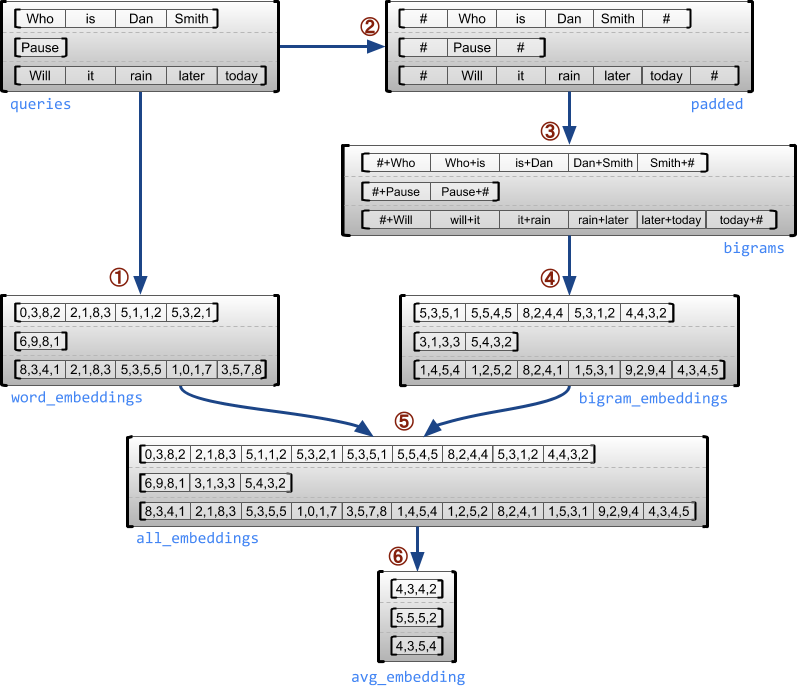"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "An_k0pX1-PVt"
},
"source": [
"## 不规则维度和均匀维度\n",
"\n",
"***不规则维度***是切片可能具有不同长度的维度。例如,`rt=[[3, 1, 4, 1], [], [5, 9, 2], [6], []]` 的内部(列)维度是不规则的,因为列切片 (`rt[0, :]`, ..., `rt[4, :]`) 具有不同的长度。切片全都具有相同长度的维度称为*均匀维度*。\n",
"\n",
"不规则张量的最外层维度始终是统一维度,因为它只包含一个切片(因此不可能有不同的切片长度)。其余维度可能是不规则维度,也可能是统一维度。例如,我们可以使用形状为 `[num_sentences, (num_words), embedding_size]` 的不规则张量为一批句子中的每个单词存储单词嵌入向量,其中 `(num_words)` 周围的括号表示维度是不规则维度。\n",
"\n",
"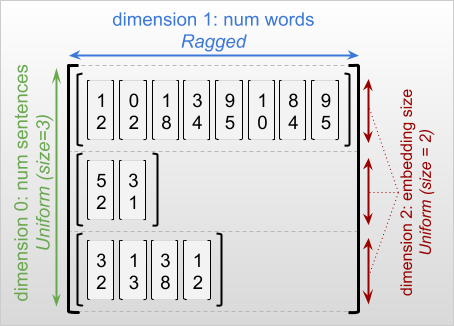\n",
"\n",
"不规则张量可以有多个不规则维度。例如,我们可以使用形状为 `[num_documents, (num_paragraphs), (num_sentences), (num_words)]` 的张量存储一批结构化文本文档(其中,括号同样用于表示不规则维度)。\n",
"\n",
"与 `tf.Tensor` 一样,不规则张量的***秩***是其总维数(包括不规则维度和均匀维度)。***潜在的不规则张量***是一个值,这个值可能是 `tf.Tensor` 或 `tf.RaggedTensor`。\n",
"\n",
"描述 RaggedTensor 的形状时,按照惯例,不规则维度会通过括号进行指示。例如,如上面所见,存储一批句子中每个单词的单词嵌入向量的三维 RaggedTensor 的形状可以写为 `[num_sentences, (num_words), embedding_size]`。\n",
"\n",
"`RaggedTensor.shape` 特性返回不规则张量的 `tf.TensorShape`,其中不规则维度的大小为 `None`:"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 22,
"metadata": {
"id": "M2Wzx4JEIvmb"
},
"outputs": [
{
"data": {
"text/plain": [
"TensorShape([2, None])"
]
},
"execution_count": 22,
"metadata": {},
"output_type": "execute_result"
}
],
"source": [
"tf.ragged.constant([[\"Hi\"], [\"How\", \"are\", \"you\"]]).shape"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "G9tfJOeFlijE"
},
"source": [
"可以使用方法 `tf.RaggedTensor.bounding_shape` 查找给定 `RaggedTensor` 的紧密边界形状:"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 23,
"metadata": {
"id": "5DHaqXHxlWi0"
},
"outputs": [
{
"name": "stdout",
"output_type": "stream",
"text": [
"tf.Tensor([2 3], shape=(2,), dtype=int64)\n"
]
}
],
"source": [
"print(tf.ragged.constant([[\"Hi\"], [\"How\", \"are\", \"you\"]]).bounding_shape())"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "V8e7x95UcLS6"
},
"source": [
"## 不规则张量和稀疏张量对比\n",
"\n",
"不规则张量*不*应该被认为是一种稀疏张量。尤其是,稀疏张量是以紧凑的格式对相同数据建模的 *`tf.Tensor` 的高效编码*;而不规则张量是对扩展的数据类建模的 *`tf.Tensor` 的扩展*。这种区别在定义运算时至关重要:\n",
"\n",
"- 对稀疏张量或密集张量应用某一运算应当始终获得相同结果。\n",
"- 对不规则张量或稀疏张量应用某一运算可能获得不同结果。\n",
"\n",
"一个说明性的示例是,考虑如何为不规则张量和稀疏张量定义 `concat`、`stack` 和 `tile` 之类的数组运算。连接不规则张量时,会将每一行连在一起,形成一个具有组合长度的行:\n",
"\n",
"\n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 24,
"metadata": {
"id": "ush7IGUWLXIn"
},
"outputs": [
{
"name": "stdout",
"output_type": "stream",
"text": [
"\n"
]
}
],
"source": [
"ragged_x = tf.ragged.constant([[\"John\"], [\"a\", \"big\", \"dog\"], [\"my\", \"cat\"]])\n",
"ragged_y = tf.ragged.constant([[\"fell\", \"asleep\"], [\"barked\"], [\"is\", \"fuzzy\"]])\n",
"print(tf.concat([ragged_x, ragged_y], axis=1))"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "pvQzZG8zMoWa"
},
"source": [
"但连接稀疏张量时,相当于连接相应的密集张量,如以下示例所示(其中 Ø 表示缺失的值):\n",
"\n",
"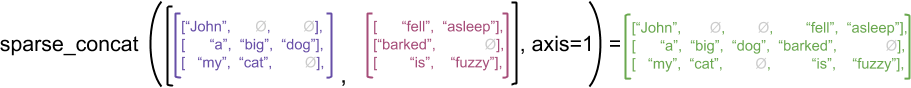\n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 25,
"metadata": {
"id": "eTIhGayQL0gI"
},
"outputs": [
{
"name": "stdout",
"output_type": "stream",
"text": [
"tf.Tensor(\n",
"[[b'John' b'' b'' b'fell' b'asleep']\n",
" [b'a' b'big' b'dog' b'barked' b'']\n",
" [b'my' b'cat' b'' b'is' b'fuzzy']], shape=(3, 5), dtype=string)\n"
]
}
],
"source": [
"sparse_x = ragged_x.to_sparse()\n",
"sparse_y = ragged_y.to_sparse()\n",
"sparse_result = tf.sparse.concat(sp_inputs=[sparse_x, sparse_y], axis=1)\n",
"print(tf.sparse.to_dense(sparse_result, ''))"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "Vl8eQN8pMuYx"
},
"source": [
"另一个说明为什么这种区别非常重要的示例是,考虑一个运算(如 `tf.reduce_mean`)的“每行平均值”的定义。对于不规则张量,一行的平均值是该行的值总和除以该行的宽度。但对于稀疏张量来说,一行的平均值是该行的值总和除以稀疏张量的总宽度(大于等于最长行的宽度)。\n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "u4yjxcK7IPXc"
},
"source": [
"## TensorFlow API"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "VoZGwFQjIYU5"
},
"source": [
"### Keras\n",
"\n",
"[tf.keras](https://tensorflow.google.cn/guide/keras) 是 TensorFlow 的高级 API,用于构建和训练深度学习模型。通过在 `tf.keras.Input` 或 `tf.keras.layers.InputLayer` 上设置 `ragged=True`,不规则张量可以作为输入传送到 Keras 模型。不规则张量还可以在 Keras 层之间传递,并由 Keras 模型返回。以下示例显示了一个使用不规则张量训练的小 LSTM 模型。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 26,
"metadata": {
"id": "pHls7hQVJlk5"
},
"outputs": [
{
"ename": "TypeError",
"evalue": "Input() got an unexpected keyword argument 'ragged'",
"output_type": "error",
"traceback": [
"\u001b[0;31m---------------------------------------------------------------------------\u001b[0m",
"\u001b[0;31mTypeError\u001b[0m Traceback (most recent call last)",
"Cell \u001b[0;32mIn[26], line 16\u001b[0m\n\u001b[1;32m 12\u001b[0m hashed_words \u001b[38;5;241m=\u001b[39m tf\u001b[38;5;241m.\u001b[39mstrings\u001b[38;5;241m.\u001b[39mto_hash_bucket_fast(words, hash_buckets)\n\u001b[1;32m 14\u001b[0m \u001b[38;5;66;03m# Build the Keras model.\u001b[39;00m\n\u001b[1;32m 15\u001b[0m keras_model \u001b[38;5;241m=\u001b[39m tf\u001b[38;5;241m.\u001b[39mkeras\u001b[38;5;241m.\u001b[39mSequential([\n\u001b[0;32m---> 16\u001b[0m tf\u001b[38;5;241m.\u001b[39mkeras\u001b[38;5;241m.\u001b[39mlayers\u001b[38;5;241m.\u001b[39mInput(shape\u001b[38;5;241m=\u001b[39m[\u001b[38;5;28;01mNone\u001b[39;00m], dtype\u001b[38;5;241m=\u001b[39mtf\u001b[38;5;241m.\u001b[39mint64, ragged\u001b[38;5;241m=\u001b[39m\u001b[38;5;28;01mTrue\u001b[39;00m),\n\u001b[1;32m 17\u001b[0m tf\u001b[38;5;241m.\u001b[39mkeras\u001b[38;5;241m.\u001b[39mlayers\u001b[38;5;241m.\u001b[39mEmbedding(hash_buckets, \u001b[38;5;241m16\u001b[39m),\n\u001b[1;32m 18\u001b[0m tf\u001b[38;5;241m.\u001b[39mkeras\u001b[38;5;241m.\u001b[39mlayers\u001b[38;5;241m.\u001b[39mLSTM(\u001b[38;5;241m32\u001b[39m, use_bias\u001b[38;5;241m=\u001b[39m\u001b[38;5;28;01mFalse\u001b[39;00m),\n\u001b[1;32m 19\u001b[0m tf\u001b[38;5;241m.\u001b[39mkeras\u001b[38;5;241m.\u001b[39mlayers\u001b[38;5;241m.\u001b[39mDense(\u001b[38;5;241m32\u001b[39m),\n\u001b[1;32m 20\u001b[0m tf\u001b[38;5;241m.\u001b[39mkeras\u001b[38;5;241m.\u001b[39mlayers\u001b[38;5;241m.\u001b[39mActivation(tf\u001b[38;5;241m.\u001b[39mnn\u001b[38;5;241m.\u001b[39mrelu),\n\u001b[1;32m 21\u001b[0m tf\u001b[38;5;241m.\u001b[39mkeras\u001b[38;5;241m.\u001b[39mlayers\u001b[38;5;241m.\u001b[39mDense(\u001b[38;5;241m1\u001b[39m)\n\u001b[1;32m 22\u001b[0m ])\n\u001b[1;32m 24\u001b[0m keras_model\u001b[38;5;241m.\u001b[39mcompile(loss\u001b[38;5;241m=\u001b[39m\u001b[38;5;124m'\u001b[39m\u001b[38;5;124mbinary_crossentropy\u001b[39m\u001b[38;5;124m'\u001b[39m, optimizer\u001b[38;5;241m=\u001b[39m\u001b[38;5;124m'\u001b[39m\u001b[38;5;124mrmsprop\u001b[39m\u001b[38;5;124m'\u001b[39m)\n\u001b[1;32m 25\u001b[0m keras_model\u001b[38;5;241m.\u001b[39mfit(hashed_words, is_question, epochs\u001b[38;5;241m=\u001b[39m\u001b[38;5;241m5\u001b[39m)\n",
"\u001b[0;31mTypeError\u001b[0m: Input() got an unexpected keyword argument 'ragged'"
]
}
],
"source": [
"# Task: predict whether each sentence is a question or not.\n",
"sentences = tf.constant(\n",
" ['What makes you think she is a witch?',\n",
" 'She turned me into a newt.',\n",
" 'A newt?',\n",
" 'Well, I got better.'])\n",
"is_question = tf.constant([True, False, True, False])\n",
"\n",
"# Preprocess the input strings.\n",
"hash_buckets = 1000\n",
"words = tf.strings.split(sentences, ' ')\n",
"hashed_words = tf.strings.to_hash_bucket_fast(words, hash_buckets)\n",
"\n",
"# Build the Keras model.\n",
"keras_model = tf.keras.Sequential([\n",
" tf.keras.layers.Input(shape=[None], dtype=tf.int64, ragged=True),\n",
" tf.keras.layers.Embedding(hash_buckets, 16),\n",
" tf.keras.layers.LSTM(32, use_bias=False),\n",
" tf.keras.layers.Dense(32),\n",
" tf.keras.layers.Activation(tf.nn.relu),\n",
" tf.keras.layers.Dense(1)\n",
"])\n",
"\n",
"keras_model.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy', optimizer='rmsprop')\n",
"keras_model.fit(hashed_words, is_question, epochs=5)\n",
"print(keras_model.predict(hashed_words))"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "8B_sdlt6Ij61"
},
"source": [
"### tf.Example\n",
"\n",
"[tf.Example](https://tensorflow.google.cn/tutorials/load_data/tfrecord) 是 TensorFlow 数据的标准 [protobuf](https://developers.google.com/protocol-buffers/) 编码。使用 `tf.Example` 编码的数据往往包括可变长度特征。例如,以下代码定义了一批具有不同特征长度的四条 `tf.Example` 消息:"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "xsiglYM7TXGr"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"import google.protobuf.text_format as pbtext\n",
"\n",
"def build_tf_example(s):\n",
" return pbtext.Merge(s, tf.train.Example()).SerializeToString()\n",
"\n",
"example_batch = [\n",
" build_tf_example(r'''\n",
" features {\n",
" feature {key: \"colors\" value {bytes_list {value: [\"red\", \"blue\"]} } }\n",
" feature {key: \"lengths\" value {int64_list {value: [7]} } } }'''),\n",
" build_tf_example(r'''\n",
" features {\n",
" feature {key: \"colors\" value {bytes_list {value: [\"orange\"]} } }\n",
" feature {key: \"lengths\" value {int64_list {value: []} } } }'''),\n",
" build_tf_example(r'''\n",
" features {\n",
" feature {key: \"colors\" value {bytes_list {value: [\"black\", \"yellow\"]} } }\n",
" feature {key: \"lengths\" value {int64_list {value: [1, 3]} } } }'''),\n",
" build_tf_example(r'''\n",
" features {\n",
" feature {key: \"colors\" value {bytes_list {value: [\"green\"]} } }\n",
" feature {key: \"lengths\" value {int64_list {value: [3, 5, 2]} } } }''')]"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "szUuXFvtUL2o"
},
"source": [
"您可以使用 `tf.io.parse_example` 解析此编码数据,它采用序列化字符串的张量和特征规范字典,并将字典映射特征名称返回给张量。要将可变长度特征读入不规则张量,我们只需在特征规范字典中使用 `tf.io.RaggedFeature`:"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "xcdaIbYVT4mo"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"feature_specification = {\n",
" 'colors': tf.io.RaggedFeature(tf.string),\n",
" 'lengths': tf.io.RaggedFeature(tf.int64),\n",
"}\n",
"feature_tensors = tf.io.parse_example(example_batch, feature_specification)\n",
"for name, value in feature_tensors.items():\n",
" print(\"{}={}\".format(name, value))"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "IK9X_8rXVr8h"
},
"source": [
"`tf.io.RaggedFeature` 还可用于读取具有多个不规则维度的特征。有关详情,请参阅 [API 文档](https://tensorflow.google.cn/api_docs/python/tf/io/RaggedFeature)。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "UJowRhlxIX0R"
},
"source": [
"### 数据集\n",
"\n",
"[tf.data](https://tensorflow.google.cn/guide/data) 是一个 API,可用于通过简单的可重用代码块构建复杂的输入流水线。它的核心数据结构是 `tf.data.Dataset`,表示一系列元素,每个元素包含一个或多个分量。 "
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "fBml1m2G2vO9"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Helper function used to print datasets in the examples below.\n",
"def print_dictionary_dataset(dataset):\n",
" for i, element in enumerate(dataset):\n",
" print(\"Element {}:\".format(i))\n",
" for (feature_name, feature_value) in element.items():\n",
" print('{:>14} = {}'.format(feature_name, feature_value))"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "gEu_H1Sp2jz1"
},
"source": [
"#### 使用不规则张量构建数据集\n",
"\n",
"可以采用从 `tf.Tensor` 或 NumPy `array` 构建数据集时使用的方法,如 `Dataset.from_tensor_slices`,从不规则张量构建数据集:"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "BuelF_y2mEq9"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(feature_tensors)\n",
"print_dictionary_dataset(dataset)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "mC-QNkJc56De"
},
"source": [
"注:`Dataset.from_generator` 目前还不支持不规则张量,但不久后将会支持这种张量。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "K0UKvBLf1VMu"
},
"source": [
"#### 批处理和取消批处理具有不规则张量的数据集\n",
"\n",
"可以使用 `Dataset.batch` 方法对具有不规则张量的数据集进行批处理(将 *n* 个连续元素组合成单个元素)。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "lk62aRz63IZn"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"batched_dataset = dataset.batch(2)\n",
"print_dictionary_dataset(batched_dataset)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "NLSGiYEQ5A8N"
},
"source": [
"相反,可以使用 `Dataset.unbatch` 将批处理后的数据集转换为扁平数据集。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "CxLlaPw_5Je4"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"unbatched_dataset = batched_dataset.unbatch()\n",
"print_dictionary_dataset(unbatched_dataset)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "YzpLQFh33q0N"
},
"source": [
"#### 对具有可变长度非不规则张量的数据集进行批处理\n",
"\n",
"如果您有一个包含非不规则张量的数据集,而且各个元素的张量长度不同,则可以应用 `dense_to_ragged_batch` 转换,将这些非不规则张量批处理成不规则张量:"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "PYnhERwh3_mf"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"non_ragged_dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices([1, 5, 3, 2, 8])\n",
"non_ragged_dataset = non_ragged_dataset.map(tf.range)\n",
"batched_non_ragged_dataset = non_ragged_dataset.apply(\n",
" tf.data.experimental.dense_to_ragged_batch(2))\n",
"for element in batched_non_ragged_dataset:\n",
" print(element)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "nXFPeE-CzJ-s"
},
"source": [
"#### 转换具有不规则张量的数据集\n",
"\n",
"还可以使用 `Dataset.map` 在数据集中创建或转换不规则张量:"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "Ios1GuG-pf9U"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"def transform_lengths(features):\n",
" return {\n",
" 'mean_length': tf.math.reduce_mean(features['lengths']),\n",
" 'length_ranges': tf.ragged.range(features['lengths'])}\n",
"transformed_dataset = dataset.map(transform_lengths)\n",
"print_dictionary_dataset(transformed_dataset)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "WD2lWw3fIXrg"
},
"source": [
"### tf.function\n",
"\n",
"[tf.function](https://tensorflow.google.cn/guide/function) 是预计算 Python 函数的 TensorFlow 计算图的装饰器,它可以大幅改善 TensorFlow 代码的性能。不规则张量能够透明地与 `@tf.function` 装饰的函数一起使用。例如,以下函数对不规则张量和非不规则张量均有效:"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "PfyxgVaj_8tl"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"@tf.function\n",
"def make_palindrome(x, axis):\n",
" return tf.concat([x, tf.reverse(x, [axis])], axis)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "vcZdzvEnDEt0"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"make_palindrome(tf.constant([[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]]), axis=1)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "4WfCMIgdDMxj"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"make_palindrome(tf.ragged.constant([[1, 2], [3], [4, 5, 6]]), axis=1)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "X2p69YPOBUz8"
},
"source": [
"如果您希望为 `tf.function` 明确指定 `input_signature`,可以使用 `tf.RaggedTensorSpec` 执行此操作。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "k6-hkhdDBk6G"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"@tf.function(\n",
" input_signature=[tf.RaggedTensorSpec(shape=[None, None], dtype=tf.int32)])\n",
"def max_and_min(rt):\n",
" return (tf.math.reduce_max(rt, axis=-1), tf.math.reduce_min(rt, axis=-1))\n",
"\n",
"max_and_min(tf.ragged.constant([[1, 2], [3], [4, 5, 6]]))"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "fSs-7E0VD85q"
},
"source": [
"#### 具体函数\n",
"\n",
"[具体函数](https://tensorflow.google.cn/guide/function#obtaining_concrete_functions)封装通过 `tf.function` 构建的各个跟踪图。不规则张量可以透明地与具体函数一起使用。\n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "yyJeXJ4wFWox"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Preferred way to use ragged tensors with concrete functions (TF 2.3+):\n",
"try:\n",
" @tf.function\n",
" def increment(x):\n",
" return x + 1\n",
"\n",
" rt = tf.ragged.constant([[1, 2], [3], [4, 5, 6]])\n",
" cf = increment.get_concrete_function(rt)\n",
" print(cf(rt))\n",
"except Exception as e:\n",
" print(f\"Not supported before TF 2.3: {type(e)}: {e}\")\n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "iYLyPlatIXhh"
},
"source": [
"### SavedModel\n",
"\n",
"[SavedModel](https://tensorflow.google.cn/guide/saved_model) 是序列化 TensorFlow 程序,包括权重和计算。它可以通过 Keras 模型或自定义模型构建。在任何一种情况下,不规则张量都可以透明地与 SavedModel 定义的函数和方法一起使用。\n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "98VpBSdOgWqL"
},
"source": [
"#### 示例:保存 Keras 模型"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "D-Dg9w7Je5pU"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"import tempfile\n",
"\n",
"keras_module_path = tempfile.mkdtemp()\n",
"tf.saved_model.save(keras_model, keras_module_path)\n",
"imported_model = tf.saved_model.load(keras_module_path)\n",
"imported_model(hashed_words)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "9-7k-E92gaoR"
},
"source": [
"#### 示例:保存自定义模型\n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "Sfem1ESrdGzX"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"class CustomModule(tf.Module):\n",
" def __init__(self, variable_value):\n",
" super(CustomModule, self).__init__()\n",
" self.v = tf.Variable(variable_value)\n",
"\n",
" @tf.function\n",
" def grow(self, x):\n",
" return x * self.v\n",
"\n",
"module = CustomModule(100.0)\n",
"\n",
"# Before saving a custom model, you must ensure that concrete functions are\n",
"# built for each input signature that you will need.\n",
"module.grow.get_concrete_function(tf.RaggedTensorSpec(shape=[None, None],\n",
" dtype=tf.float32))\n",
"\n",
"custom_module_path = tempfile.mkdtemp()\n",
"tf.saved_model.save(module, custom_module_path)\n",
"imported_model = tf.saved_model.load(custom_module_path)\n",
"imported_model.grow(tf.ragged.constant([[1.0, 4.0, 3.0], [2.0]]))"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "SAxis5KBhrBN"
},
"source": [
"注:SavedModel [签名](https://tensorflow.google.cn/guide/saved_model#specifying_signatures_during_export)是具体函数。如上文的“具体函数”部分所述,从 TensorFlow 2.3 开始,只有具体函数才能正确处理不规则张量。如果您需要在先前版本的 TensorFlow 中使用 SavedModel 签名,建议您将不规则张量分解成其分量张量。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "cRcHzS6pcHYC"
},
"source": [
"## 重载运算符\n",
"\n",
"`RaggedTensor` 类会重载标准 Python 算术和比较运算符,使其易于执行基本的逐元素数学:"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "skScd37P-PVu"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"x = tf.ragged.constant([[1, 2], [3], [4, 5, 6]])\n",
"y = tf.ragged.constant([[1, 1], [2], [3, 3, 3]])\n",
"print(x + y)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "XEGgbZHV-PVw"
},
"source": [
"由于重载运算符执行逐元素计算,因此所有二进制运算的输入必须具有相同的形状,或者可以广播至相同的形状。在最简单的广播情况下,单个标量与不规则张量中的每个值逐元素组合:"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "IYybEEWc-PVx"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"x = tf.ragged.constant([[1, 2], [3], [4, 5, 6]])\n",
"print(x + 3)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "okGb9dIi-PVz"
},
"source": [
"有关更高级用例的讨论,请参阅**广播**部分。\n",
"\n",
"不规则张量重载与正常 `Tensor` 相同的一组运算符:一元运算符 `-`、`~` 和 `abs()`;二元运算符 `+`、`-`、`*`、`/`、`//`、`%`、`**`、`&`、`|`、`^`、`==`、`<`、`<=`、`>` 和 `>=`。\n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "f2anbs6ZnFtl"
},
"source": [
"## 索引\n",
"\n",
"不规则张量支持 Python 风格的索引,包括多维索引和切片。以下示例使用二维和三维不规则张量演示了不规则张量索引。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "XuEwmC3t_ITL"
},
"source": [
"### 索引示例:二维不规则张量"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "MbSRZRDz-PV1"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"queries = tf.ragged.constant(\n",
" [['Who', 'is', 'George', 'Washington'],\n",
" ['What', 'is', 'the', 'weather', 'tomorrow'],\n",
" ['Goodnight']])"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "2HRs2xhh-vZE"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"print(queries[1]) # A single query"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "EFfjZV7YA3UH"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"print(queries[1, 2]) # A single word"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "VISRPQSdA3xn"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"print(queries[1:]) # Everything but the first row"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "J1PpSyKQBMng"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"print(queries[:, :3]) # The first 3 words of each query"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "ixrhHmJBeidy"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"print(queries[:, -2:]) # The last 2 words of each query"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "cnOP6Vza-PV4"
},
"source": [
"### 索引示例:三维不规则张量"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "8VbqbKcE-PV6"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"rt = tf.ragged.constant([[[1, 2, 3], [4]],\n",
" [[5], [], [6]],\n",
" [[7]],\n",
" [[8, 9], [10]]])"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "f9WPVWf4grVp"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"print(rt[1]) # Second row (2D RaggedTensor)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "ad8FGJoABjQH"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"print(rt[3, 0]) # First element of fourth row (1D Tensor)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "MPPr-a-bBjFE"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"print(rt[:, 1:3]) # Items 1-3 of each row (3D RaggedTensor)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "6SIDeoIUBi4z"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"print(rt[:, -1:]) # Last item of each row (3D RaggedTensor)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "_d3nBh1GnWvU"
},
"source": [
"`RaggedTensor` 支持多维索引和切片,但有一个限制:不允许索引到不规则维度。这种情况会出现问题,因为指示的值可能在某些行中存在,而在其他行中不存在。在这种情况下,我们不知道是应该 (1) 引发 `IndexError`;(2) 使用默认值;还是 (3) 跳过该值并返回一个行数比开始时少的张量。根据 [Python 的指导原则](https://www.python.org/dev/peps/pep-0020/)(“当面对不明确的情况时,不要尝试去猜测”),我们目前不允许此运算。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "IsWKETULAJbN"
},
"source": [
"## 张量类型转换\n",
"\n",
"`RaggedTensor` 类定义了可用于在 `RaggedTensor` 与 `tf.Tensor` 或 `tf.SparseTensors` 之间转换的方法:"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "INnfmZGcBoU_"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"ragged_sentences = tf.ragged.constant([\n",
" ['Hi'], ['Welcome', 'to', 'the', 'fair'], ['Have', 'fun']])"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "__iJ4iXtkGOx"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# RaggedTensor -> Tensor\n",
"print(ragged_sentences.to_tensor(default_value='', shape=[None, 10]))"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "-rfiyYqne8QN"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Tensor -> RaggedTensor\n",
"x = [[1, 3, -1, -1], [2, -1, -1, -1], [4, 5, 8, 9]]\n",
"print(tf.RaggedTensor.from_tensor(x, padding=-1))"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "41WAZLXNnbwH"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"#RaggedTensor -> SparseTensor\n",
"print(ragged_sentences.to_sparse())"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "S8MkYo2hfVhj"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# SparseTensor -> RaggedTensor\n",
"st = tf.SparseTensor(indices=[[0, 0], [2, 0], [2, 1]],\n",
" values=['a', 'b', 'c'],\n",
" dense_shape=[3, 3])\n",
"print(tf.RaggedTensor.from_sparse(st))"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "qx025sNMkAHH"
},
"source": [
"## 评估不规则张量\n",
"\n",
"要访问不规则张量中的值,您可以:\n",
"\n",
"1. 使用 `tf.RaggedTensor.to_list()` 将不规则张量转换为嵌套 Python 列表。\n",
"2. 使用 `tf.RaggedTensor.numpy()` 将不规则张量转换为 NumPy 数组,该数组的值为嵌套 NumPy 数组。\n",
"3. 使用 `tf.RaggedTensor.values` 和 `tf.RaggedTensor.row_splits` 属性,或 `tf.RaggedTensor.row_lengths()` 和 `tf.RaggedTensor.value_rowids()` 等行分区方法,将不规则张量分解成其分量。\n",
"4. 使用 Python 索引从不规则张量中选择值。\n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "uMm1WMkc-PV_"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"rt = tf.ragged.constant([[1, 2], [3, 4, 5], [6], [], [7]])\n",
"print(\"Python list:\", rt.to_list())\n",
"print(\"NumPy array:\", rt.numpy())\n",
"print(\"Values:\", rt.values.numpy())\n",
"print(\"Splits:\", rt.row_splits.numpy())\n",
"print(\"Indexed value:\", rt[1].numpy())"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "J87jMZa0M_YW"
},
"source": [
"## 不规则形状\n",
"\n",
"张量的形状指定每个轴的大小。例如 `[[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]]` 的形状为 `[3, 2]`,因为有 3 行 2 列。TensorFlow 有两种独立但相关的方式来描述形状:\n",
"\n",
"- ***静态形状***:关于静态已知的轴大小的信息(例如,在跟踪 `tf.function` 时)。可以部分指定。\n",
"\n",
"- ***动态形状***:有关轴大小的运行时信息。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "IOETE_OLPLZo"
},
"source": [
"### 静态形状\n",
"\n",
"张量的静态形状包含有关其轴大小的信息,这些信息在计算图构造时是已知的。对于 `tf.Tensor` 和 `tf.RaggedTensor`,它可以使用 `.shape` 属性获得,并使用 `tf.TensorShape` 进行编码:"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "btGDjT4uNgQy"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"x = tf.constant([[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]])\n",
"x.shape # shape of a tf.tensor"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "__OgvmrGPEjq"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"rt = tf.ragged.constant([[1], [2, 3], [], [4]])\n",
"rt.shape # shape of a tf.RaggedTensor"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "9EWnQd3qPWaw"
},
"source": [
"不规则维度的静态形状始终为 `None`(即未指定)。然而,反过来则不成立。如果 `TensorShape` 维度为 `None`,则可能表明维度是不规则的,*或者*表明维度是统一的,但其大小不是静态已知的。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "75E9YXYMNfne"
},
"source": [
"### 动态形状\n",
"\n",
"张量的动态形状包含有关其轴大小的信息,这些信息在计算图运行时是已知的。它使用 `tf.shape` 运算构造。对于 `tf.Tensor`,`tf.shape` 将形状作为一维整数 `Tensor` 返回,其中 `tf.shape(x)[i]` 为轴 `i` 的大小。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "kWJ7Cn1EQTD_"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"x = tf.constant([['a', 'b'], ['c', 'd'], ['e', 'f']])\n",
"tf.shape(x)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "BeZEfxwmRcSv"
},
"source": [
"然而,一维 `Tensor` 的表达性不足以描述 `tf.RaggedTensor` 的形状。相反,不规则张量的动态形状使用专用类型 `tf.experimental.DynamicRaggedShape` 进行编码。在下面的示例中,`tf.shape(rt)` 返回的 `DynamicRaggedShape` 表示不规则张量有 4 行,长度分别为 1、3、0 和 2:"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "nZc2wqgQQUFU"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"rt = tf.ragged.constant([[1], [2, 3, 4], [], [5, 6]])\n",
"rt_shape = tf.shape(rt)\n",
"print(rt_shape)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "EphU60YvTf98"
},
"source": [
"#### 动态形状:运算\n",
"\n",
"`DynamicRaggedShape` 可与大多数需要形状的 TensorFlow 运算一起使用,包括 `tf.reshape`、`tf.zeros`、`tf.ones`、`tf.fill`、`tf.broadcast_dynamic_shape` 和 `tf.broadcast_to`。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "pclAODLXT6Gr"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"print(f\"tf.reshape(x, rt_shape) = {tf.reshape(x, rt_shape)}\")\n",
"print(f\"tf.zeros(rt_shape) = {tf.zeros(rt_shape)}\")\n",
"print(f\"tf.ones(rt_shape) = {tf.ones(rt_shape)}\")\n",
"print(f\"tf.fill(rt_shape, 9) = {tf.fill(rt_shape, 'x')}\")"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "rNP_3_btRAHj"
},
"source": [
"#### 动态形状:索引和切片\n",
"\n",
"`DynamicRaggedShape` 也可以被索引以获得统一维度的大小。例如,我们可以使用 `tf.shape(rt)[0]` 找到不规则张量中的行数(就像我们对非不规则张量做的那样):"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "MzQvPhsxS6HN"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"rt_shape[0]"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "wvr2iT6zS_e8"
},
"source": [
"但是,使用索引来尝试检索不规则维度的大小是一种错误,因为它没有单一的大小。(由于 `RaggedTensor` 会跟踪哪些轴是不规则的,仅在 Eager execution 期间或跟踪 `tf.function` 时会引发此错误;在执行具体函数时永远不会引发此错误。)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "HgGMk0LeTGik"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"try:\n",
" rt_shape[1]\n",
"except ValueError as e:\n",
" print(\"Got expected ValueError:\", e)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "5QUsdawGU0SM"
},
"source": [
"此外,也可以对 `DynamicRaggedShape` 进行切片,前提是切片从轴 `0` 开始,或者仅包含密集维度。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "APT72EaBU70t"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"rt_shape[:1]"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "a-Wl9IrQXcdY"
},
"source": [
"#### 动态形状:编码\n",
"\n",
"`DynamicRaggedShape` 使用两个字段进行编码:\n",
"\n",
"- `inner_shape`:一个整数向量,给出了密集 `tf.Tensor` 的形状。\n",
"- `row_partitions`:`tf.experimental.RowPartition` 对象的列表,描述了应当如何对该内部形状的最外层维度进行分区以添加不规则轴。\n",
"\n",
"有关行分区的更多信息,请参阅下面的“不规则张量编码”部分以及 `tf.experimental.RowPartition` 的 API 文档。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "jfeY9tTcV_zL"
},
"source": [
"#### 动态形状:构造\n",
"\n",
"`DynamicRaggedShape` 最常通过将 `tf.shape` 应用于 `RaggedTensor` 来构造,但也可以直接构造:"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "NSRgD667WwIZ"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"tf.experimental.DynamicRaggedShape(\n",
" row_partitions=[tf.experimental.RowPartition.from_row_lengths([5, 3, 2])],\n",
" inner_shape=[10, 8])"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "EjzVjs9MXIIA"
},
"source": [
"如果所有行的长度都是静态已知的,`DynamicRaggedShape.from_lengths` 也可用于构造动态不规则形状。(这对于测试和演示代码特别有用,因为极少会静态已知不规则维度的长度)。\n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "gMxCzADUYIjY"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"tf.experimental.DynamicRaggedShape.from_lengths([4, (2, 1, 0, 8), 12])"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "EdljbNPq-PWS"
},
"source": [
"### 广播\n",
"\n",
"广播是使具有不同形状的张量获得兼容形状以便进行逐元素运算的过程。有关广播的更多背景信息,请参阅:\n",
"\n",
"- [NumPy:广播](https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/user/basics.broadcasting.html)\n",
"- `tf.broadcast_dynamic_shape`\n",
"- `tf.broadcast_to`\n",
"\n",
"广播两个输入 `x` 和 `y`,使其具有兼容形状的基本步骤是:\n",
"\n",
"1. 如果 `x` 和 `y` 没有相同的维数,则增加外层维度(使用大小 1),直至它们具有相同的维数。\n",
"\n",
"2. 对于 `x` 和 `y` 的大小不同的每一个维度:\n",
"\n",
"- 如果 `x` 或 `y` 在 `d` 维中的大小为 `1`,则在 `d` 维中重复其值以匹配其他输入的大小。\n",
"- 否则,引发异常(`x` 和 `y` 非广播兼容)。\n",
"\n",
"其中,均匀维度中一个张量的大小是一个数字(跨该维的切片大小);不规则维度中一个张量的大小是切片长度列表(跨该维的所有切片)。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "-S2hOUWx-PWU"
},
"source": [
"#### 广播示例"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "0n095XdR-PWU"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# x (2D ragged): 2 x (num_rows)\n",
"# y (scalar)\n",
"# result (2D ragged): 2 x (num_rows)\n",
"x = tf.ragged.constant([[1, 2], [3]])\n",
"y = 3\n",
"print(x + y)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "0SVYk5AP-PWW"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# x (2d ragged): 3 x (num_rows)\n",
"# y (2d tensor): 3 x 1\n",
"# Result (2d ragged): 3 x (num_rows)\n",
"x = tf.ragged.constant(\n",
" [[10, 87, 12],\n",
" [19, 53],\n",
" [12, 32]])\n",
"y = [[1000], [2000], [3000]]\n",
"print(x + y)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "MsfBMD80s8Ux"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# x (3d ragged): 2 x (r1) x 2\n",
"# y (2d ragged): 1 x 1\n",
"# Result (3d ragged): 2 x (r1) x 2\n",
"x = tf.ragged.constant(\n",
" [[[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]],\n",
" [[7, 8]]],\n",
" ragged_rank=1)\n",
"y = tf.constant([[10]])\n",
"print(x + y)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "rEj5QVfnva0t"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# x (3d ragged): 2 x (r1) x (r2) x 1\n",
"# y (1d tensor): 3\n",
"# Result (3d ragged): 2 x (r1) x (r2) x 3\n",
"x = tf.ragged.constant(\n",
" [\n",
" [\n",
" [[1], [2]],\n",
" [],\n",
" [[3]],\n",
" [[4]],\n",
" ],\n",
" [\n",
" [[5], [6]],\n",
" [[7]]\n",
" ]\n",
" ],\n",
" ragged_rank=2)\n",
"y = tf.constant([10, 20, 30])\n",
"print(x + y)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "uennZ64Aqftb"
},
"source": [
"下面是一些不广播的形状示例:"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "UpI0FlfL4Eim"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# x (2d ragged): 3 x (r1)\n",
"# y (2d tensor): 3 x 4 # trailing dimensions do not match\n",
"x = tf.ragged.constant([[1, 2], [3, 4, 5, 6], [7]])\n",
"y = tf.constant([[1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7, 8], [9, 10, 11, 12]])\n",
"try:\n",
" x + y\n",
"except tf.errors.InvalidArgumentError as exception:\n",
" print(exception)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "qGq1zOT4zMoc"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# x (2d ragged): 3 x (r1)\n",
"# y (2d ragged): 3 x (r2) # ragged dimensions do not match.\n",
"x = tf.ragged.constant([[1, 2, 3], [4], [5, 6]])\n",
"y = tf.ragged.constant([[10, 20], [30, 40], [50]])\n",
"try:\n",
" x + y\n",
"except tf.errors.InvalidArgumentError as exception:\n",
" print(exception)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "CvLae5vMqeji"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# x (3d ragged): 3 x (r1) x 2\n",
"# y (3d ragged): 3 x (r1) x 3 # trailing dimensions do not match\n",
"x = tf.ragged.constant([[[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]],\n",
" [[7, 8], [9, 10]]])\n",
"y = tf.ragged.constant([[[1, 2, 0], [3, 4, 0], [5, 6, 0]],\n",
" [[7, 8, 0], [9, 10, 0]]])\n",
"try:\n",
" x + y\n",
"except tf.errors.InvalidArgumentError as exception:\n",
" print(exception)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "m0wQkLfV-PWa"
},
"source": [
"## RaggedTensor 编码\n",
"\n",
"不规则张量使用 `RaggedTensor` 类进行编码。在内部,每个 `RaggedTensor` 包含:\n",
"\n",
"- 一个 `values` 张量,它将可变长度行连接成扁平列表。\n",
"- 一个 `row_partition`,它指示如何将这些扁平值分成各行。\n",
"\n",
"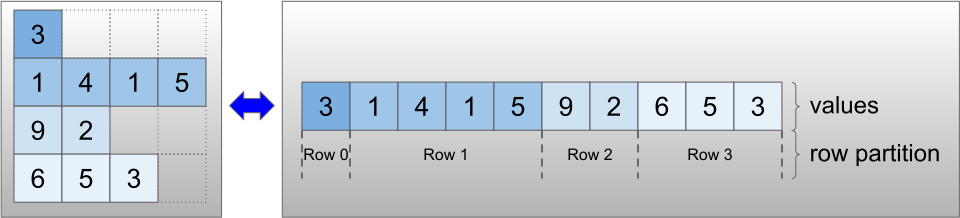\n",
"\n",
"可以使用四种不同的编码存储 `row_partition`:\n",
"\n",
"- `row_splits` 是一个整型向量,用于指定行之间的拆分点。\n",
"- `value_rowids` 是一个整型向量,用于指定每个值的行索引。\n",
"- `row_lengths` 是一个整型向量,用于指定每一行的长度。\n",
"- `uniform_row_length` 是一个整型标量,用于指定所有行的单个长度。\n",
"\n",
"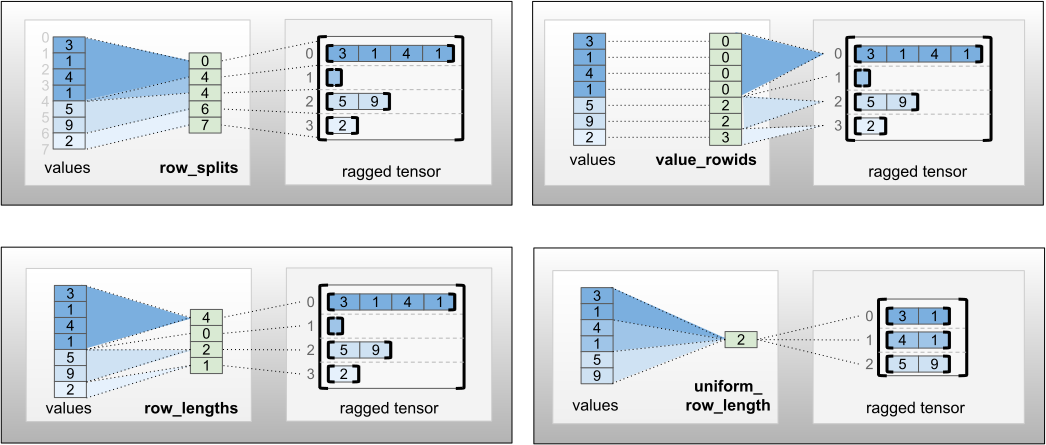\n",
"\n",
"整型标量 `nrows` 还可以包含在 `row_partition` 编码中,以考虑具有 `value_rowids` 的空尾随行或具有 `uniform_row_length` 的空行。\n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "MrLgMu0gPuo-"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"rt = tf.RaggedTensor.from_row_splits(\n",
" values=[3, 1, 4, 1, 5, 9, 2],\n",
" row_splits=[0, 4, 4, 6, 7])\n",
"print(rt)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "wEfZOKwN1Ra_"
},
"source": [
"选择为行分区使用哪种编码由不规则张量在内部进行管理,以提高某些环境下的效率。特别要指出的是,不同行分区方案的某些优点和缺点是:\n",
"\n",
"- **高效索引**:`row_splits` 编码可以实现不规则张量的恒定时间索引和切片。\n",
"- **高效连接**:`row_lengths` 编码在连接不规则张量时更有效,因为当两个张量连接在一起时,行长度不会改变。\n",
"- **较小的编码大小**:`value_rowids` 编码在存储具有大量空行的不规则张量时更有效,因为张量的大小只取决于值的总数。另一方面,`row_splits` 和 `row_lengths` 编码在存储具有较长行的不规则张量时更有效,因为它们每行只需要一个标量值。\n",
"- **兼容性**:`value_rowids` 方案与 tf.segment_sum 等运算使用的[分段](https://tensorflow.google.cn/api_docs/python/tf/math#about_segmentation)格式相匹配。`row_limits` 方案与 `tf.sequence_mask` 等运算使用的格式相匹配。\n",
"- **均匀维**:如下文所述,`uniform_row_length` 编码用于对具有均匀维的不规则张量进行编码。"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "bpB7xKoUPtU6"
},
"source": [
"### 多个不规则维度\n",
"\n",
"具有多个不规则维度的不规则张量通过为 `values` 张量使用嵌套 `RaggedTensor` 进行编码。每个嵌套 `RaggedTensor` 都会增加一个不规则维度。\n",
"\n",
"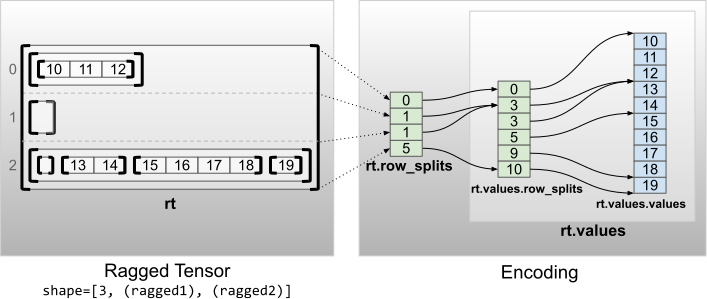\n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "yy3IGT2a-PWb"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"rt = tf.RaggedTensor.from_row_splits(\n",
" values=tf.RaggedTensor.from_row_splits(\n",
" values=[10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19],\n",
" row_splits=[0, 3, 3, 5, 9, 10]),\n",
" row_splits=[0, 1, 1, 5])\n",
"print(rt)\n",
"print(\"Shape: {}\".format(rt.shape))\n",
"print(\"Number of partitioned dimensions: {}\".format(rt.ragged_rank))"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "5HqEEDzk-PWc"
},
"source": [
"工厂函数 `tf.RaggedTensor.from_nested_row_splits` 可用于通过提供一个 `row_splits` 张量列表,直接构造具有多个不规则维度的 RaggedTensor:"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "AKYhtFcT-PWd"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"rt = tf.RaggedTensor.from_nested_row_splits(\n",
" flat_values=[10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19],\n",
" nested_row_splits=([0, 1, 1, 5], [0, 3, 3, 5, 9, 10]))\n",
"print(rt)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "BqAfbkAC56m0"
},
"source": [
"### 不规则秩和扁平值\n",
"\n",
"不规则张量的***不规则秩***是底层 `values` 张量的分区次数(即 `RaggedTensor` 对象的嵌套深度)。最内层的 `values` 张量称为其 ***flat_values***。在以下示例中,`conversations` 具有 ragged_rank=3,其 `flat_values` 为具有 24 个字符串的一维 `Tensor`:\n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "BXp-Tt2bClem"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# shape = [batch, (paragraph), (sentence), (word)]\n",
"conversations = tf.ragged.constant(\n",
" [[[[\"I\", \"like\", \"ragged\", \"tensors.\"]],\n",
" [[\"Oh\", \"yeah?\"], [\"What\", \"can\", \"you\", \"use\", \"them\", \"for?\"]],\n",
" [[\"Processing\", \"variable\", \"length\", \"data!\"]]],\n",
" [[[\"I\", \"like\", \"cheese.\"], [\"Do\", \"you?\"]],\n",
" [[\"Yes.\"], [\"I\", \"do.\"]]]])\n",
"conversations.shape"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "DZUMrgxXFd5s"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"assert conversations.ragged_rank == len(conversations.nested_row_splits)\n",
"conversations.ragged_rank # Number of partitioned dimensions."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "xXLSNpS0Fdvp"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"conversations.flat_values.numpy()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "uba2EnAY-PWf"
},
"source": [
"### 均匀内层维度\n",
"\n",
"具有均匀内层维度的不规则张量通过为 flat_values(即最内层 `values`)使用多维 `tf.Tensor` 进行编码。\n",
"\n",
"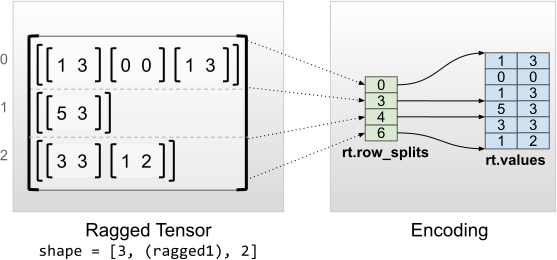"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "z2sHwHdy-PWg"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"rt = tf.RaggedTensor.from_row_splits(\n",
" values=[[1, 3], [0, 0], [1, 3], [5, 3], [3, 3], [1, 2]],\n",
" row_splits=[0, 3, 4, 6])\n",
"print(rt)\n",
"print(\"Shape: {}\".format(rt.shape))\n",
"print(\"Number of partitioned dimensions: {}\".format(rt.ragged_rank))\n",
"print(\"Flat values shape: {}\".format(rt.flat_values.shape))\n",
"print(\"Flat values:\\n{}\".format(rt.flat_values))"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {
"id": "WoGRKd50x_qz"
},
"source": [
"### 均匀非内层维度\n",
"\n",
"具有均匀非内层维度的不规则张量通过使用 `uniform_row_length` 对行分区进行编码。\n",
"\n",
"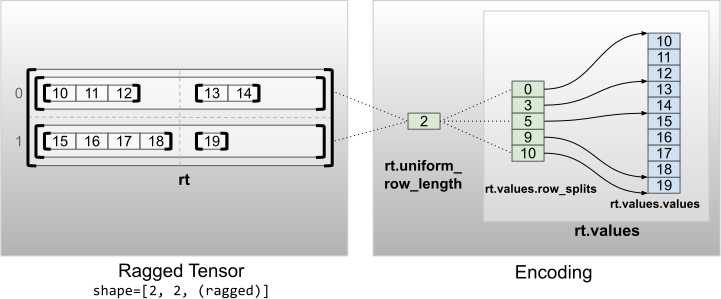"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"id": "70q1aCKwySgS"
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"rt = tf.RaggedTensor.from_uniform_row_length(\n",
" values=tf.RaggedTensor.from_row_splits(\n",
" values=[10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19],\n",
" row_splits=[0, 3, 5, 9, 10]),\n",
" uniform_row_length=2)\n",
"print(rt)\n",
"print(\"Shape: {}\".format(rt.shape))\n",
"print(\"Number of partitioned dimensions: {}\".format(rt.ragged_rank))"
]
}
],
"metadata": {
"colab": {
"collapsed_sections": [],
"name": "ragged_tensor.ipynb",
"toc_visible": true
},
"kernelspec": {
"display_name": "xxx",
"language": "python",
"name": "python3"
},
"language_info": {
"codemirror_mode": {
"name": "ipython",
"version": 3
},
"file_extension": ".py",
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
"name": "python",
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
"version": "3.12.2"
}
},
"nbformat": 4,
"nbformat_minor": 0
}
 在 TensorFlow.org 上查看
在 TensorFlow.org 上查看  在 Google Colab 中运行
在 Google Colab 中运行  在 Github 上查看源代码
在 Github 上查看源代码 下载笔记本
下载笔记本  在 TensorFlow.org 上查看
在 TensorFlow.org 上查看  在 Google Colab 中运行
在 Google Colab 中运行  在 Github 上查看源代码
在 Github 上查看源代码 下载笔记本
下载笔记本